- What Exactly Is an Event Count?
- Types of Events That Generate Count Data
- Event Count vs Event Count Per User
- Why Event Count Matters for Your Website?
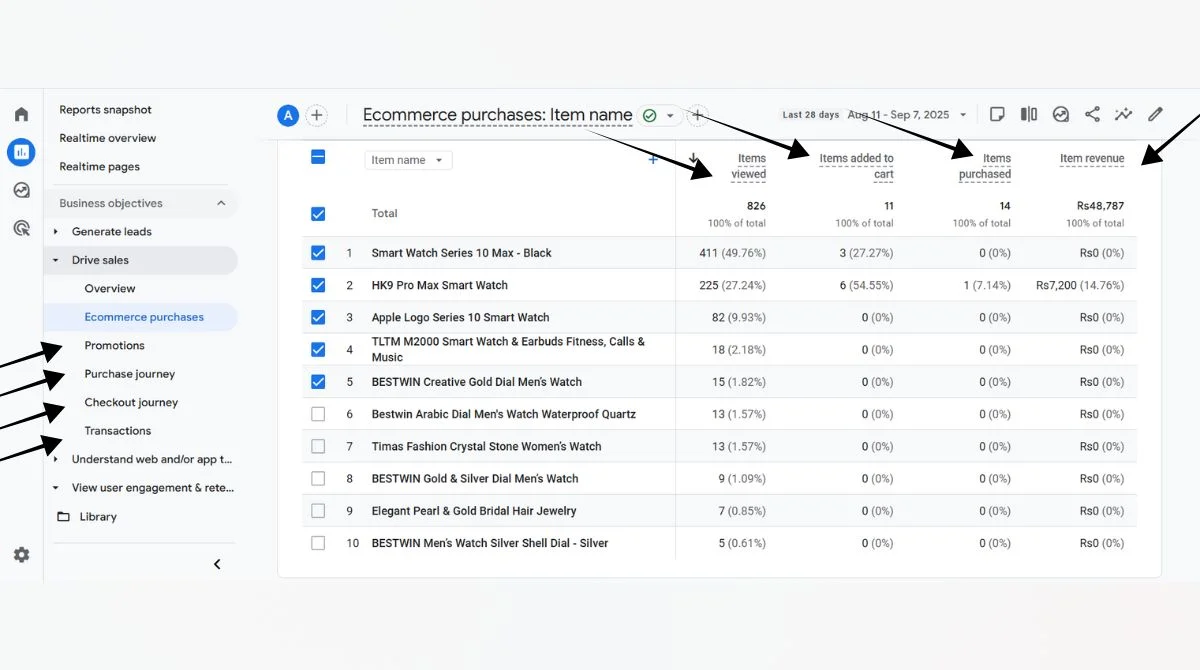
- How to Find Event Count in GA4?
- Common Event Count Scenarios
- Best Practices for Event Count Analysis
- Key Events and Conversion Tracking
- Event Count Limitations to Consider
- Optimizing Your Website Based on Event Count Data
- Future of Event Tracking in GA4
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Event count in Google Analytics is a crucial metric that tracks how many times users interact with specific elements on your website or app. Event Count in Google Analytics 4 (GA4) measures how often users interact with specific elements on a website within a given time span.
Think of event count as a digital counter that records every meaningful action users take on your site. Every click, form submission, video play, or download gets counted as an event.
What Exactly Is an Event Count?
In Google Analytics 4, Event Count represents how many times a specific event is activated on your website or app. An event represents any user interaction you want to track and measure.
When someone visits your website and performs actions like clicking buttons or watching videos, GA4 records each action as an event. The total number of these recorded actions becomes your event count.
Types of Events That Generate Count Data
Automatic Events
GA4 automatically tracks several events without any setup:
- Page views.
- Scroll tracking.
- Outbound link clicks.
- File downloads.
- Video engagement.
Enhanced Measurement Events
These events require enabling enhanced measurement:
- Form interactions.
- Site search.
- Video progress tracking.
- File downloads.
Custom Events
You can create custom events for specific business needs:
- Newsletter signups.
- Product purchases.
- Contact form submissions.
- Chat widget interactions.
Event Count vs Event Count Per User
Understanding the difference between these two metrics is important for accurate data analysis.
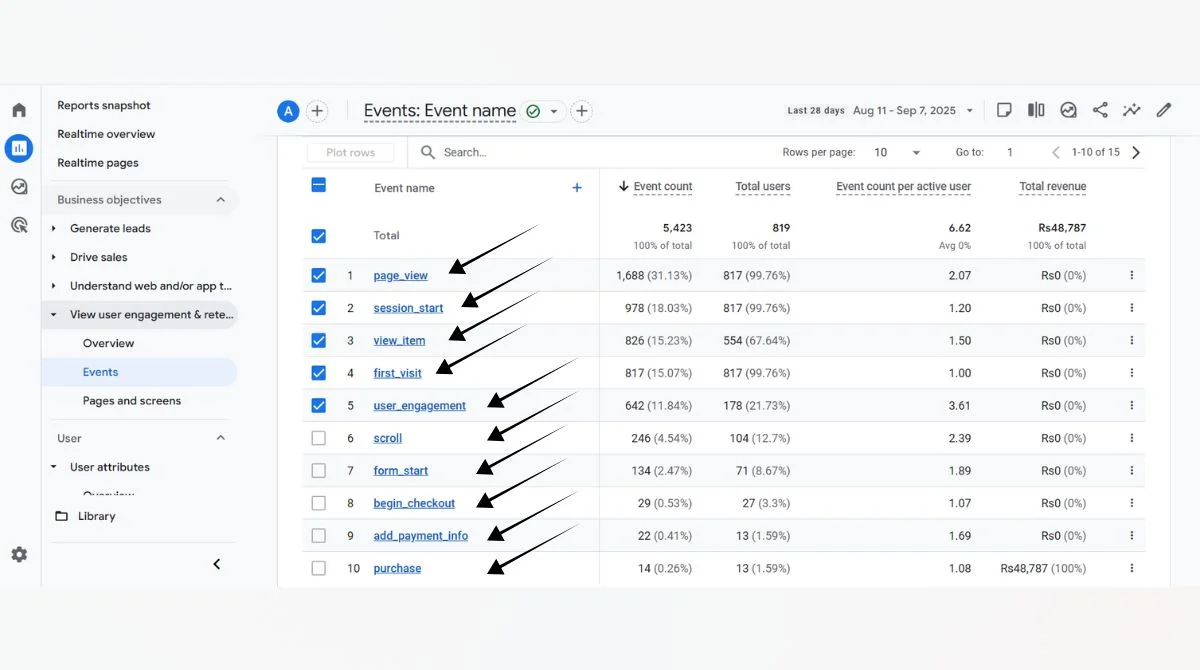
- Event Count: Shows the total number of times an event occurred across all users. Google Analytics usually displays event count as the number of times an action happens across all users.
- Event Count Per User: Shows the average number of events per individual user. GA4 also allows for granular tracking, such as Event Count Per User. This metric represents the average count of actions performed by each user.
For example, if 100 users trigger 500 events total, your event count per user would be 5.
Why Event Count Matters for Your Website?
User Engagement Measurement
Event count helps you understand how actively users engage with your content. Higher event counts often indicate more engaged visitors.
Conversion Tracking
By tracking specific events like form submissions or purchases, you can measure how well your website converts visitors into customers.
Content Performance Analysis
Event count data shows which pages, buttons, or features get the most interaction from users.
User Journey Mapping
Understanding event patterns helps you see how users navigate through your website and where they spend most time.
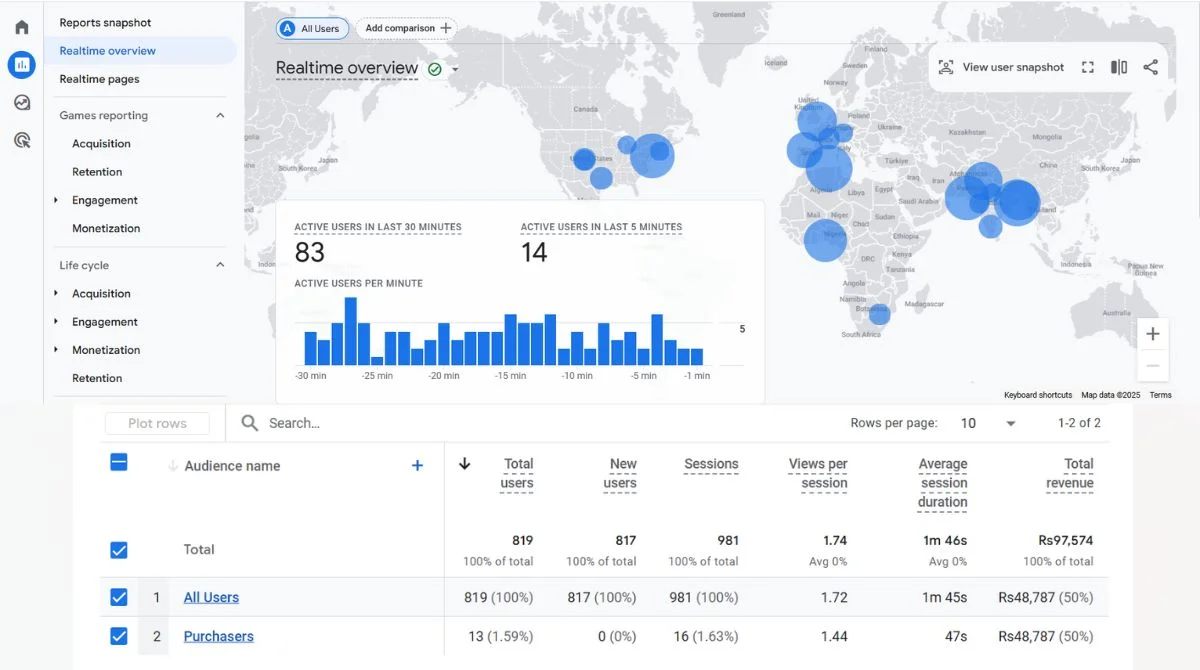
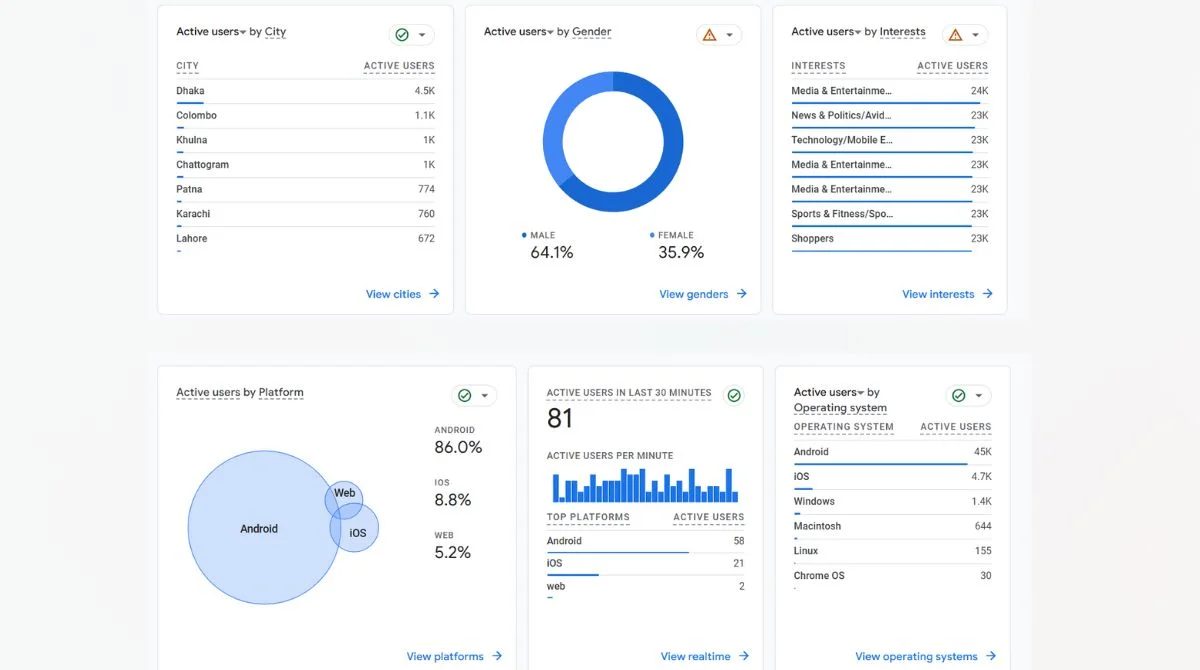
How to Find Event Count in GA4?
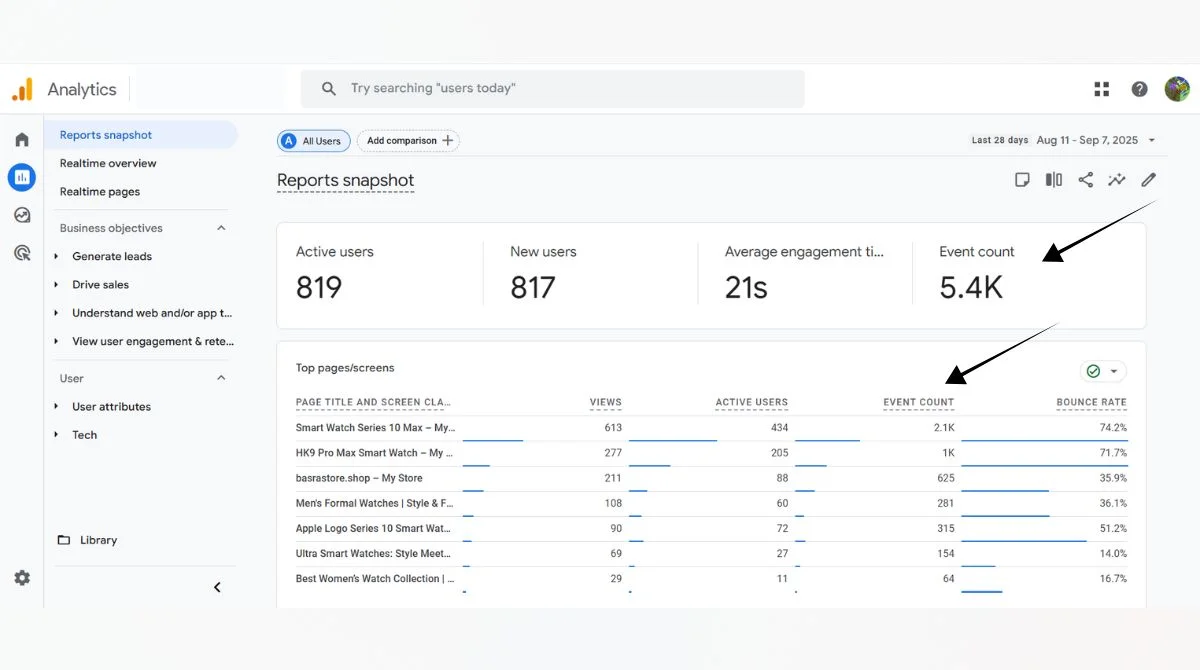
Real-Time Reports
The Event count by Event name card in the Realtime report displays each triggered event and the number of times it was initiated in the last 30 minutes by users on your website or app.
Events Report
Navigate to Reports > Engagement > Events to see detailed event count data for different time periods.
Custom Reports
Create custom reports combining event count with other metrics like user demographics or traffic sources.
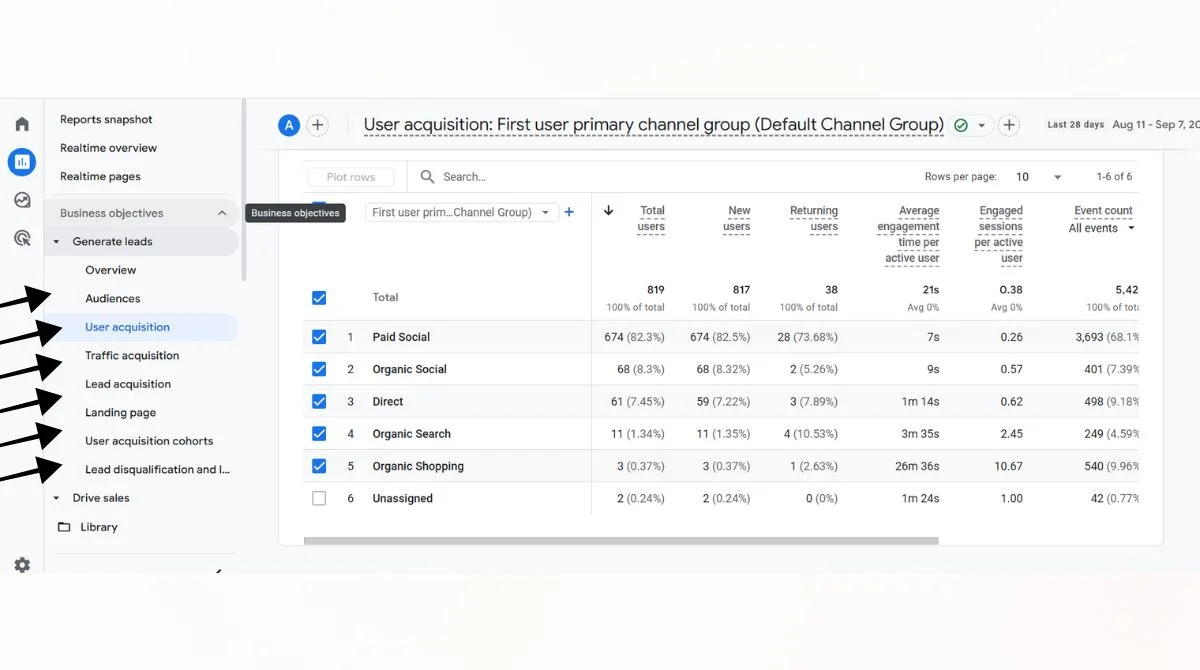
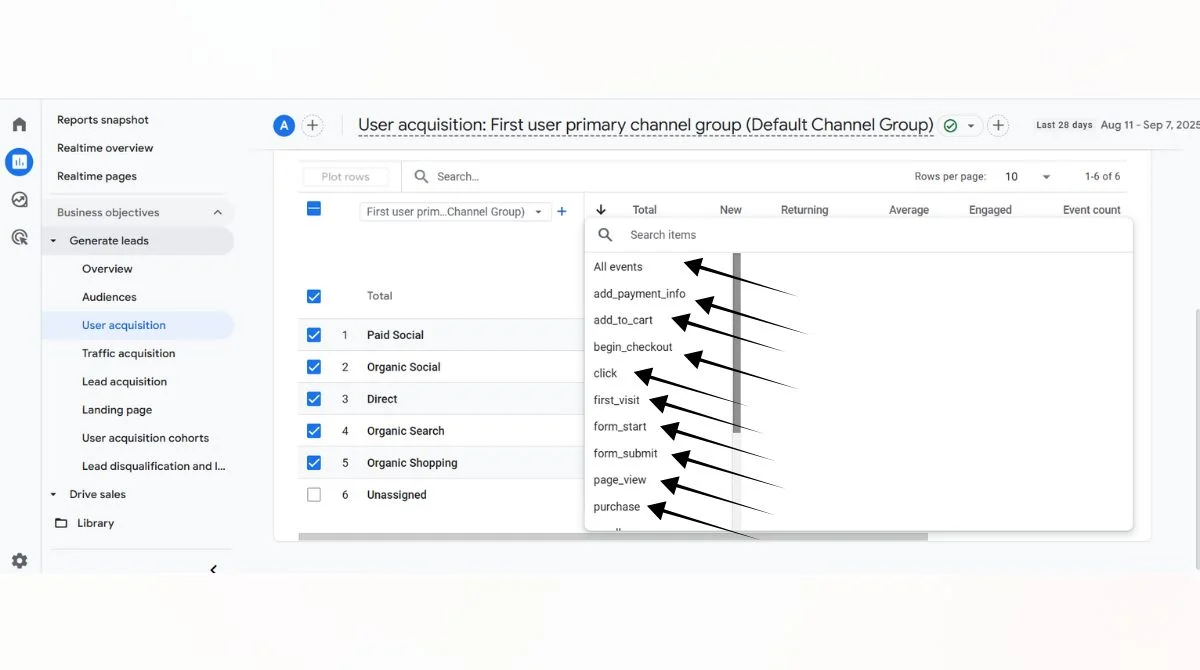
Common Event Count Scenarios
- E-commerce Websites: Track purchase events, add-to-cart actions, and product view counts to understand shopping behavior.
- Content Websites: Monitor scroll depth, article shares, and comment submissions to measure content engagement.
- Service Websites: Track contact form submissions, quote requests, and service inquiries to measure lead generation.
- SaaS Platforms: Monitor feature usage, trial signups, and subscription events to understand user adoption.
Best Practices for Event Count Analysis
- Set Clear Goals: Define what actions matter most for your business before analyzing event count data.
- Use Segments: Break down event count by user segments like new vs returning visitors or different traffic sources.
- Compare Time Periods: Look at event count trends over time to identify patterns and changes in user behavior.
- Focus on Quality Events: Prioritize tracking events that directly relate to your business objectives rather than every possible interaction.
Key Events and Conversion Tracking
A key event tracks an action that holds significant importance for the success of your business. These are formerly known as conversion events in Universal Analytics.
Key events help you focus on the most important user actions for your business success. Examples include newsletter signups, purchases, or contact form submissions.
Event Count Limitations to Consider
- Data Sampling: Large datasets might use sampling, which can affect event count accuracy for detailed analysis.
- Attribution Models: Different attribution models can affect how event counts are calculated and reported.
- Cross-Device Tracking: Users switching between devices might create separate event counts for the same person.
- Bot Traffic: Automated traffic can inflate event counts, requiring proper filtering to maintain data accuracy.
Optimizing Your Website Based on Event Count Data
Identify High-Performing Content
Use event count data to find which pages or features generate the most user engagement.
Improve Low-Performing Areas
Pages with low event counts might need better calls-to-action or more engaging content.
A/B Testing
Test different versions of pages or features and compare their event count performance.
User Experience Enhancement
Use event patterns to identify where users struggle and improve those areas.
Future of Event Tracking in GA4
Google Analytics 4 focuses heavily on event-based tracking, making event count increasingly important for understanding user behavior. GA4 records every user interaction, such as clicks, form completions, downloads, and video plays, as events. This shift means businesses need to understand event count data to make informed decisions about their digital strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the difference between event count and page views?
Event count tracks all user interactions, like clicks and form submissions, while page views only count when someone loads a new page.
Q2. Can the event count be higher than the number of users?
Yes, because one user can trigger multiple events during their visit, making the event count higher than the user count.
Q3. How often does GA4 update event count data?
Real-time event count updates within minutes, while standard reports may take 24-48 hours to process completely.
Q4. Why might my event count seem low?
Low event count could indicate tracking issues, low website traffic, poor user engagement, or events not being set up properly.
Q5. Should I track every possible user interaction as an event?
No, focus on tracking events that align with your business goals to avoid data overload and maintain meaningful insights.
Conclusion
Event count in Google Analytics provides valuable insights into how users interact with your website. By understanding what event count means and how to use this data effectively, you can improve user experience, increase conversions, and grow your business. Start by identifying the most important user actions for your business, set up proper event tracking, and regularly analyze your event count data to make data-driven improvements to your website.