- What Is Local SEO vs Traditional SEO?
- 10 Key Differences Between Local SEO and Traditional SEO
- When to Choose Local SEO vs Traditional SEO?
- The Latest Google Algorithm Updates Impact
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Best Practices for Success
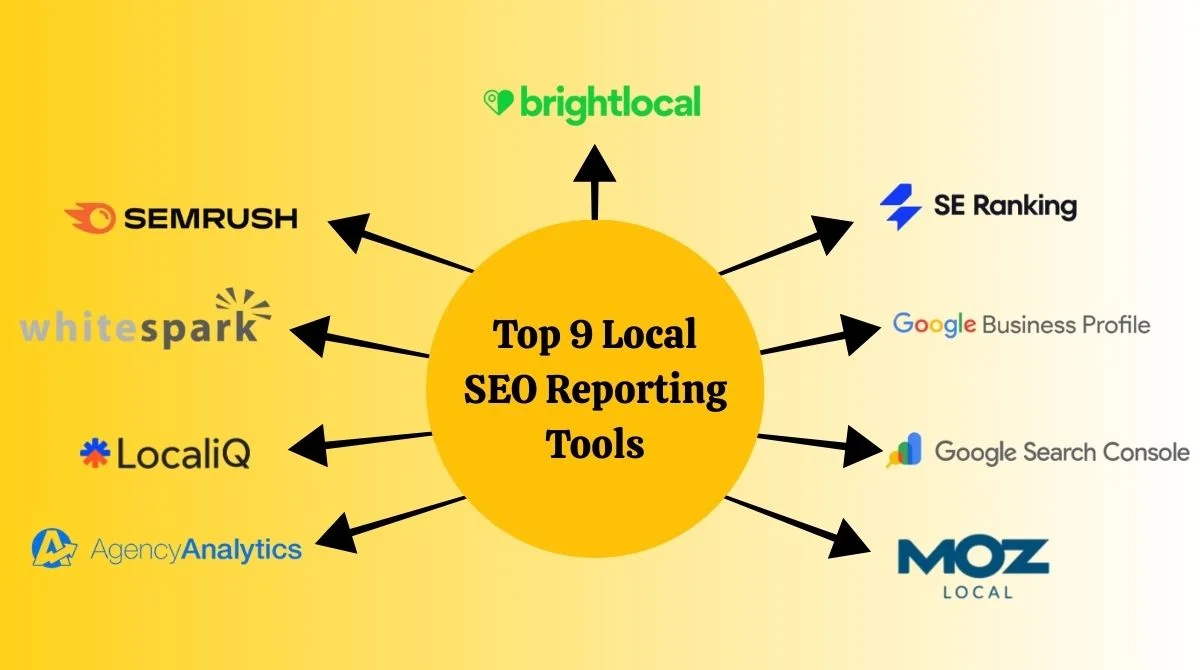
- Measuring Success: Key Metrics
- The Future of Local vs Traditional SEO
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
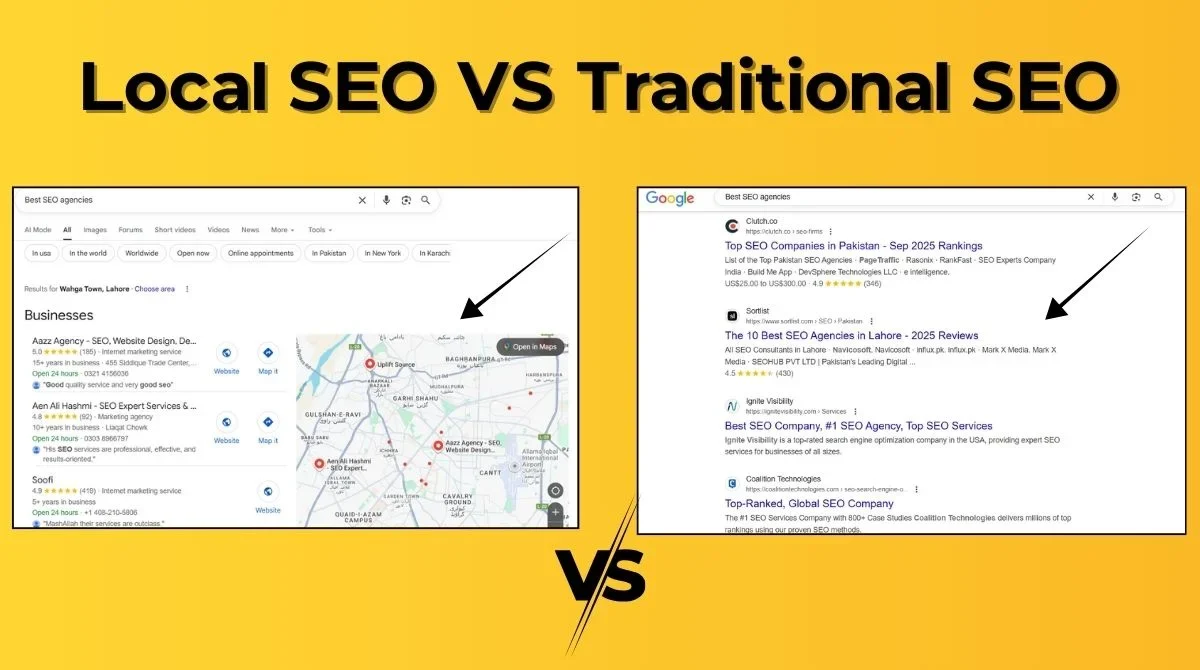
What Is Local SEO vs Traditional SEO?
Understanding the difference between local SEO and traditional SEO is crucial for any business owner. Traditional SEO focuses on improving the visibility of your website either nationally or globally, while local SEO focuses on improving the visibility of your business in local search rankings.
The main difference between traditional SEO and local SEO is who you’re trying to reach. Local SEO helps nearby customers find your business when they search for products or services in their area.
Traditional SEO targets broader audiences without geographic limitations. It aims to rank your website for relevant keywords on a national or global scale.
10 Key Differences Between Local SEO and Traditional SEO
1. Target Audience Scope
- Local SEO: Targets customers within a specific geographic area. Your goal is to attract people who can physically visit your business or use your local services.
- Traditional SEO: Larger, location non-specific (think national or global) audiences, such as those targeted by ecommerce brands, will be the target of traditional SEO.

2. Search Intent Focus
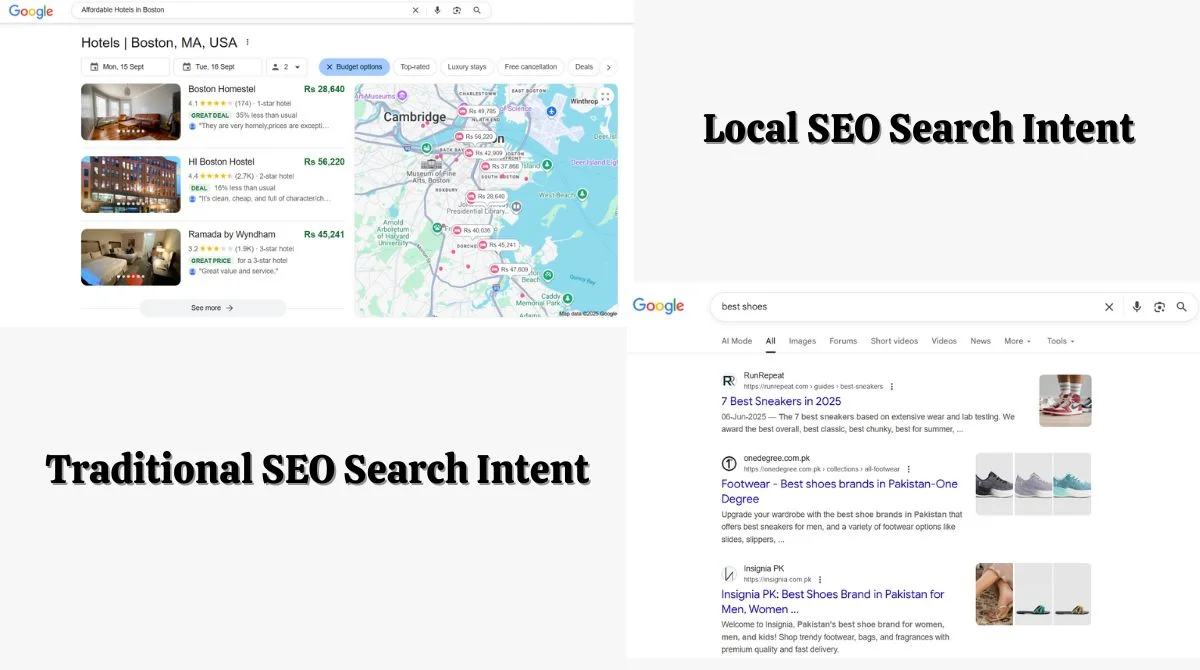
- Local SEO: It focuses exclusively on optimizing your efforts to maximize your reach among local searchers. For instance, you plan a trip and search for ‘Affordable Hotels in Boston’.
- Traditional SEO: Focuses on broad search queries without geographic modifiers. Users search for general information, products, or services without location-specific intent.
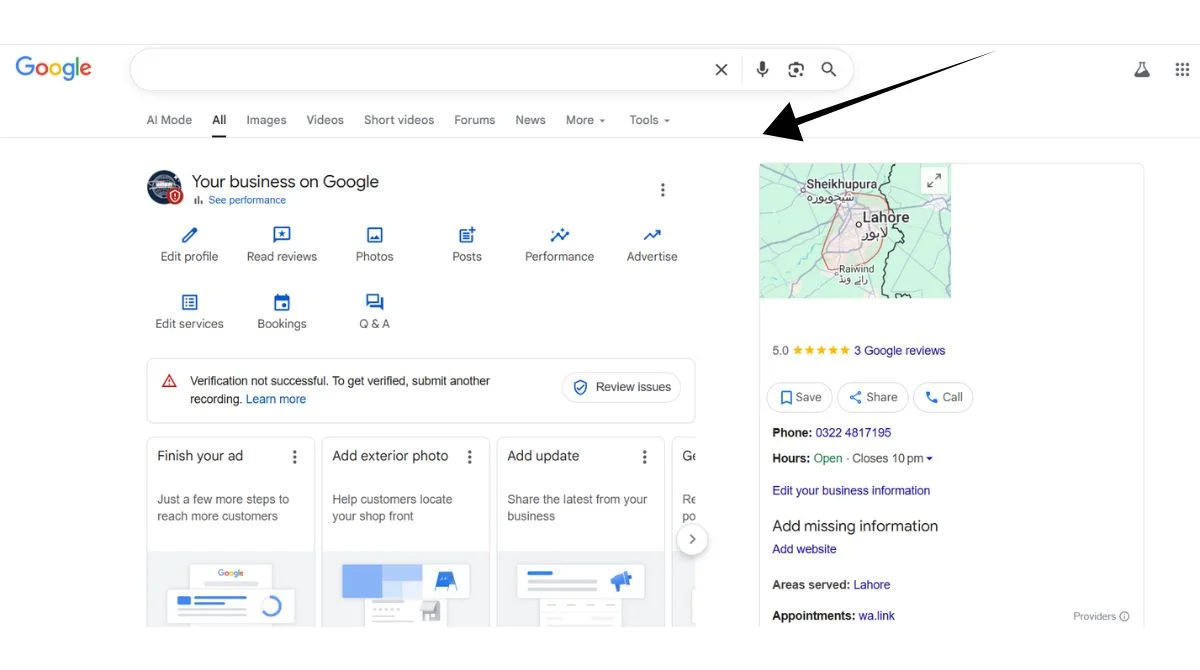
3. Google My Business Importance
- Local SEO: Google My Business profile is essential. It appears in local search results, Google Maps, and provides crucial business information like hours, phone number, and reviews.
- Traditional SEO: Google My Business is not a ranking factor. The focus remains on website optimization and content quality.
4. Citation Building Strategy
- Local SEO: Requires consistent NAP (Name, Address, Phone) citations across local directories, review sites, and industry-specific platforms.
- Traditional SEO: Citations are not necessary. The focus is on high-authority backlinks from relevant websites regardless of location.

5. Content Strategy Approach
- Local SEO: Content should include local keywords, community events, local news, and area-specific information that resonates with nearby customers.
- Traditional SEO: Content targets broader topics without geographic limitations. The goal is to provide valuable information to users worldwide.
6. Review Management Priority
- Local SEO: Search engines now consider the number of reviews, their quality, how recent they are, and similar review signals as important ranking factors.
- Traditional SEO: Reviews are less critical for rankings. User-generated content and social signals matter more than specific review platforms.
7. Link Building Tactics
- Local SEO: Local businesses can make excellent use of geography to help them discover link opportunities. For example, a local chimney sweep might earn links for industry associations in their state or country.
- Traditional SEO: Link building focuses on domain authority and relevance without geographic considerations. High-quality backlinks from authoritative sites are the priority.
8. Mobile Optimization Importance
- Local SEO: Mobile optimization for SEO in 2025 requires more than simple responsiveness. Local searches happen predominantly on mobile devices when users are on the go.
- Traditional SEO: Mobile optimization is important, but not as critical as local SEO. Desktop and mobile traffic patterns vary more significantly.
9. Competition Analysis
- Local SEO: Competitors are primarily other local businesses within your service area. You compete with nearby companies offering similar services.
- Traditional SEO: Competition includes websites globally. You compete with established brands, content publishers, and e-commerce sites worldwide.
10. Ranking Factors Weight
- Local SEO: Peak-time traffic now influences rankings. Businesses that experience higher engagement during busy hours tend to rank better. Reviews, video content, and interactions with Google Posts help increase time spent on a profile.
- Traditional SEO: The #1 factor in Google’s algorithm remains Consistent Publication of Satisfying Content. Google keeps favoring websites that regularly publish useful and valuable content.
When to Choose Local SEO vs Traditional SEO?
Choose Local SEO If:
- You have a physical business location.
- Your customers visit your store or office.
- You provide services within a specific geographic area.
- You want to appear in Google Maps results.
- Most of your revenue comes from local customers.
Choose Traditional SEO If:
- You sell products or services online globally.
- Your business operates without geographic limitations.
- You want to build a national or international brand.
- Your target audience is spread across different locations.
- You focus on content marketing and thought leadership.
The Latest Google Algorithm Updates Impact
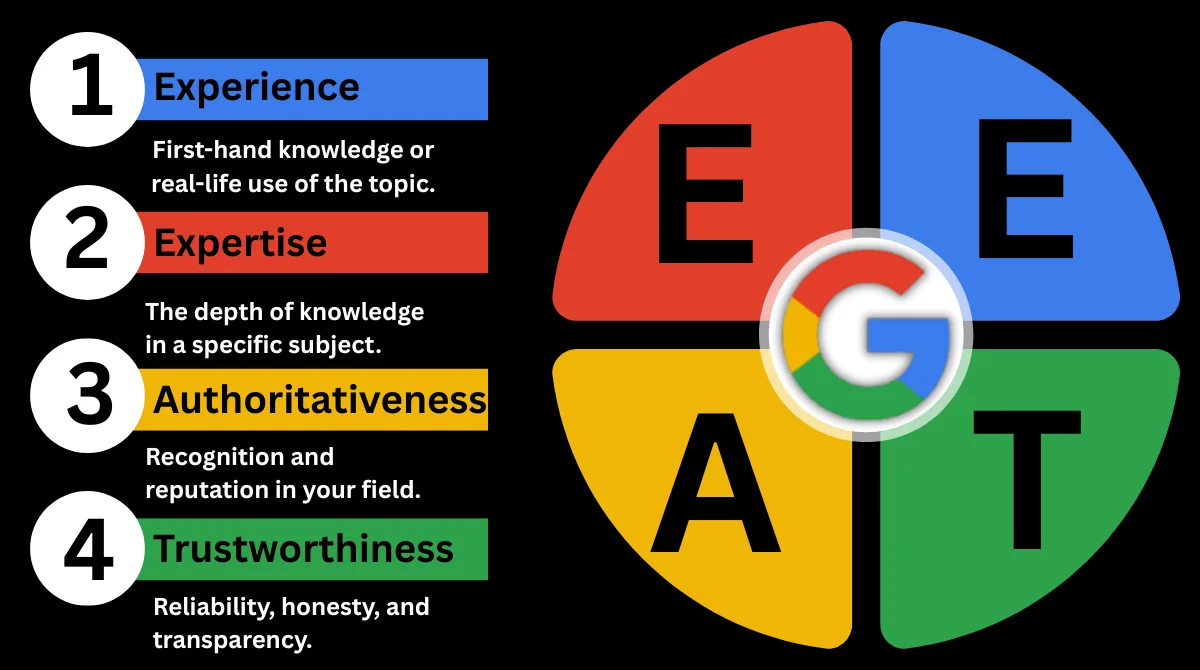
This June 2025 Google core algorithm update emphasizes topical authority, E E A T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trust), and prepares for the wider spread of AI-driven features, like AI Overviews.
Both local and traditional SEO strategies need to adapt to these changes. By prioritizing user experience, high-quality content, AI adoption, and new technologies, businesses can sustain and boost their search rankings.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Local SEO Mistakes:
- Inconsistent NAP information across platforms.
- Ignoring Google My Business optimization.
- Not responding to customer reviews.
- Overlooking local keyword research.
Traditional SEO Mistakes:
- Focusing only on keyword density.
- Ignoring user experience signals.
- Building low-quality backlinks.
- Not optimizing for featured snippets.
Best Practices for Success
Local SEO Best Practices:
- Optimize your Google My Business profile completely.
- Encourage and manage customer reviews.
- Create location-specific landing pages.
- Build local citations consistently.
- Use local schema markup.
Traditional SEO Best Practices:
- Focus on high-quality, helpful content.
- Build authoritative backlinks.
- Optimize for user search intent.
- Improve website speed and mobile experience.
- Target featured snippets and rich results.
Measuring Success: Key Metrics
Local SEO Metrics:
- Local search rankings.
- Google My Business views and actions.
- Local citation consistency.
- Review rating and quantity.
- Local organic traffic.
Traditional SEO Metrics:
- Organic traffic growth.
- Keyword ranking positions.
- Backlink profile quality.
- Content engagement metrics.
- Conversion rates from organic traffic.
The Future of Local vs Traditional SEO
The SEO landscape continues evolving with AI-driven search features and mobile-first indexing. SEO in 2025 will be all about high-quality content, user experience, and adaptability.
With algorithm changes prioritizing helpful, relevant content, businesses must refine their strategies to maintain and improve rankings.
Both local and traditional SEO will remain important, but businesses need to understand which approach aligns with their goals and customer base.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Can I use both local SEO and traditional SEO strategies together?
Yes, many businesses successfully combine both strategies to maximize their online visibility and reach different customer segments.
Q2. How long does it take to see results from local SEO vs traditional SEO?
Local SEO typically shows results faster (3-6 months) compared to traditional SEO (6-12 months) due to less competition and more specific targeting.
Q3. Is local SEO easier than traditional SEO?
Local SEO has fewer competitors but requires managing multiple platforms like Google My Business, citations, and reviews, making it different rather than easier.
Q4. Do I need a website for local SEO?
While having a website helps, you can appear in local search results through Google My Business, though a website significantly improves your rankings and credibility.
Q5. Which type of SEO is more cost-effective?
Local SEO is often more cost-effective for small businesses due to targeted competition and lower advertising costs compared to competing nationally or globally.
Conclusion
The choice between local SEO and traditional SEO depends on your business model, target audience, and goals. Many businesses benefit from combining both strategies to maximize their online visibility. Local businesses should prioritize local SEO to capture nearby customers, while e-commerce and service-based companies with broader reach should focus on traditional SEO. Understanding these differences helps you allocate resources effectively and achieve better search engine rankings.