- What Is On Page SEO?
- Core Elements of On Page SEO
- Why On Page SEO Matters?
- On Page SEO Examples
- What Is Technical SEO?
- Core Elements of Technical SEO
- Why Technical SEO Matters?
- Technical SEO Examples
- On Page SEO vs Technical SEO: Key Differences
- Which One Should You Prioritize First
- How On Page SEO and Technical SEO Work Together?
- Common On Page SEO Mistakes to Avoid
- Common Technical SEO Mistakes to Avoid
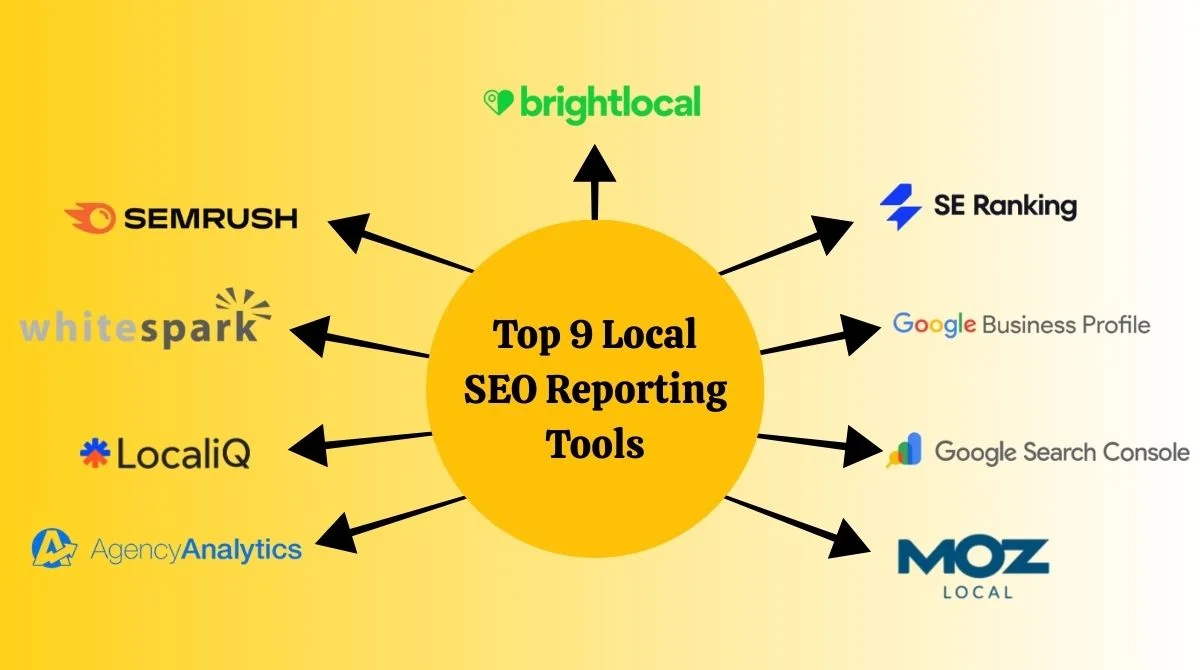
- Tools to Improve Both SEO Types
- Step-by-Step Action Plan for Beginners
- FAQ
- Conclusion
Many website owners struggle to rank because they focus on only one type of SEO. Some invest all their time into writing content and optimizing keywords, while others obsess over site speed, servers, and code. Both approaches miss the bigger picture. SEO is not a single activity it is a combination of strategies working together over time.
The real problem is simple. Without understanding the difference between on page SEO and technical SEO, you waste time, money, and effort fixing the wrong issues. This often leads to poor results, missed sales opportunities, and frustration with search engine rankings.
Whether you run a small online shop, manage a brand website, or handle investor-facing pages like conference call summaries and financial reports, understanding these two SEO pillars is critical. This guide breaks everything down step by step using simple, daily English. By the end, you will know exactly what to fix first, how both SEO types work together, and how to get measurable results year after year.
What Is On Page SEO?
On page SEO refers to all optimization activities you perform directly on your web pages to improve search rankings. This includes everything visitors can see and interact with when they land on your site. Think of it as dressing your content in a way that both humans and search engines can understand. When you write compelling headlines, structure your content with proper headings, and naturally incorporate relevant keywords, you’re practicing on page SEO. The mission here is to make your content valuable, relevant, and easy to digest for your target audience.
The beauty of on page SEO lies in its direct connection to user experience. Every change you make affects how visitors perceive your brand and whether they trust your information enough to take action. Unlike technical fixes that happen behind the scenes, on page improvements are visible and immediately impact how people engage with your content.
Core Elements of On Page SEO
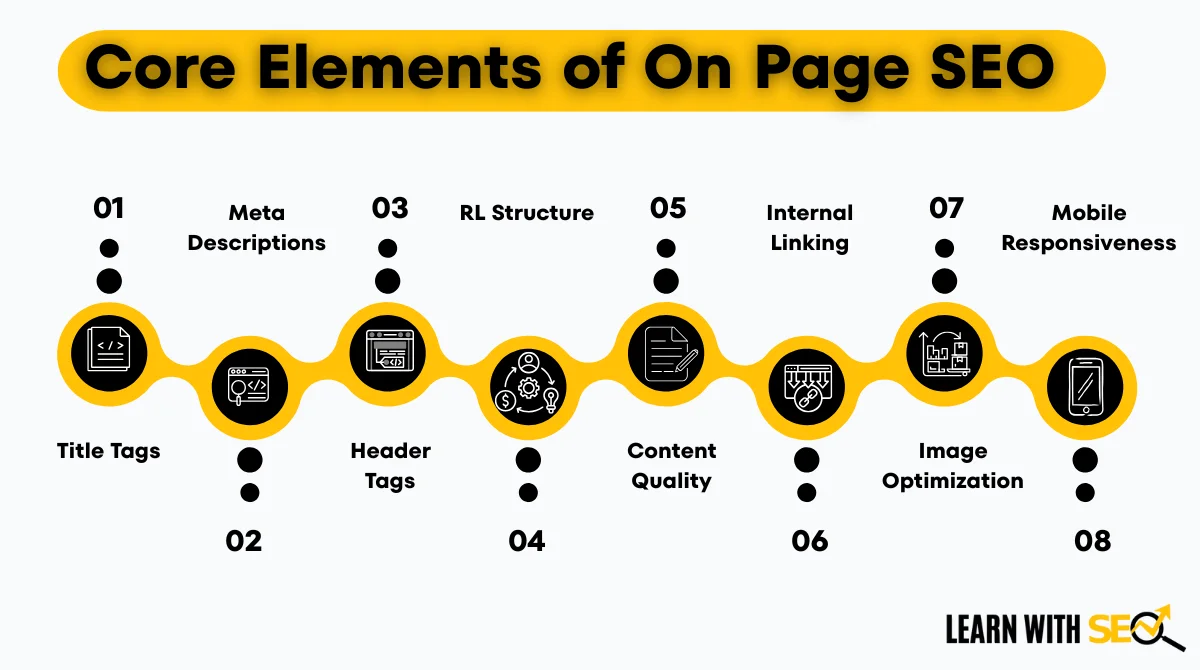
On-page SEO refers to optimizing individual web pages to rank higher in search engines and earn more relevant traffic. Here are the essential elements:
1. Title Tags
Your page title is one of the most important on-page SEO factors. It should be unique, descriptive, include your target keyword (preferably near the beginning), and stay under 60 characters to avoid truncation in search results.
2. Meta Descriptions
While not a direct ranking factor, meta descriptions influence click-through rates. Write compelling descriptions that summarize your page content, include relevant keywords naturally, and stay within 150-160 characters.
More read: Meta Title vs Meta Description
3. Header Tags (H1-H6)
Use headers to structure your content hierarchically. Your H1 should contain your main keyword and clearly indicate what the page is about. Use H2s and H3s to organize subtopics, making content easier to scan for both users and search engines.
4. URL Structure
Clean, descriptive URLs perform better than long, parameter-filled ones. Keep URLs short, include relevant keywords, use hyphens to separate words, and avoid unnecessary words like “and” or “the.”
5. Content Quality and Keyword Usage
Create comprehensive, valuable content that satisfies user intent. Use your target keywords naturally throughout the text, include related terms and synonyms (LSI keywords), and aim for depth rather than keyword stuffing. Search engines now prioritize content that genuinely answers users’ questions.
6. Internal Linking
Link to other relevant pages on your site using descriptive anchor text. This helps search engines understand your site structure, distributes page authority throughout your site, and keeps users engaged longer.
7. Image Optimization
Optimize images by using descriptive file names, adding alt text that describes the image and includes relevant keywords when appropriate, compressing files for faster loading, and using appropriate image formats.
8. Mobile Responsiveness
With mobile-first indexing, your site must work flawlessly on mobile devices. This includes responsive design, fast loading times, and touch-friendly navigation.
Focusing on these core elements creates a strong foundation for your SEO efforts. Remember that on-page SEO works best when combined with quality content, good user experience, and off-page factors like backlinks.
Why On Page SEO Matters?
On-page SEO matters because it directly influences how relevant your pages appear for specific searches. Without proper optimization, even the best content struggles to rank. Search engines need clear signals to understand what topics you cover and which queries you should appear for.
Good on-page optimization also improves user experience. When your content is well-organized with clear headings and helpful information, visitors stay longer. This engagement sends positive signals back to search engines, creating a cycle of improved rankings and traffic.
The market for online attention is competitive. Brands that master on-page SEO gain an advantage over competitors who neglect these fundamentals.
On Page SEO Examples
Real-world on-page SEO examples help clarify these concepts. A product page optimized for “running shoes for beginners” would include that phrase in the title tag, first paragraph, and at least one heading. The content would address questions beginners actually ask about choosing their first running shoes.
A blog post about email marketing might optimize for related terms like “email address collection strategies” and “contact list building.” The article would use headers to break up sections on different approaches, with internal links pointing to related guides.
An online shop category page would feature unique descriptions, optimized product titles, and helpful buyer information. Each element works together to signal relevance for shopping-related searches.
What Is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO encompasses all the behind-the-scenes optimizations that help search engines crawl, index, and understand your website. While visitors never see these elements directly, they determine whether search engines can access your content effectively. Think of technical SEO as building a solid foundation for your house without it, nothing else matters because the structure won’t stand. This includes site speed optimization, mobile responsiveness, proper indexing, secure connections, and structured data implementation.
The scope of technical SEO extends beyond simple fixes. It involves understanding how search engine bots navigate your site, identifying barriers that prevent proper crawling, and implementing solutions that improve overall site health. When technical issues exist, even the best content struggles to rank because search engines either can’t find it or can’t properly interpret it.
Core Elements of Technical SEO
Technical SEO focuses on optimizing your website’s infrastructure to help search engines crawl, index, and understand your site more effectively. Here are the fundamental elements:
1. Website Crawling and Indexing
Search engines use bots to crawl and index web pages. A site must be easily accessible so bots can discover content without issues. Proper use of robots.txt and correct index settings ensure important pages are indexed while unnecessary pages are excluded.
2. XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap acts like a roadmap for search engines. It helps them understand the structure of the website and find important pages faster. A clean and updated sitemap improves indexing, especially for large or newly launched websites.
3. Site Architecture
A well-organized site structure makes navigation simple for both users and search engines. Pages should be logically grouped and reachable within a few clicks. Clear architecture improves crawl efficiency and distributes link authority properly.
4. Mobile-Friendliness
Google uses mobile-first indexing, meaning it primarily uses the mobile version of your site for ranking. Ensure responsive design that adapts to all screen sizes, implement touch-friendly navigation with adequate button spacing, avoid intrusive interstitials that block content, and test your site using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool.
5. Robots.txt File
This file tells search engines which pages they can and cannot crawl. Place it in your root directory, use it to block crawling of duplicate or low-value pages, avoid accidentally blocking important pages, and be cautious as blocking doesn’t prevent indexing if other sites link to blocked pages.
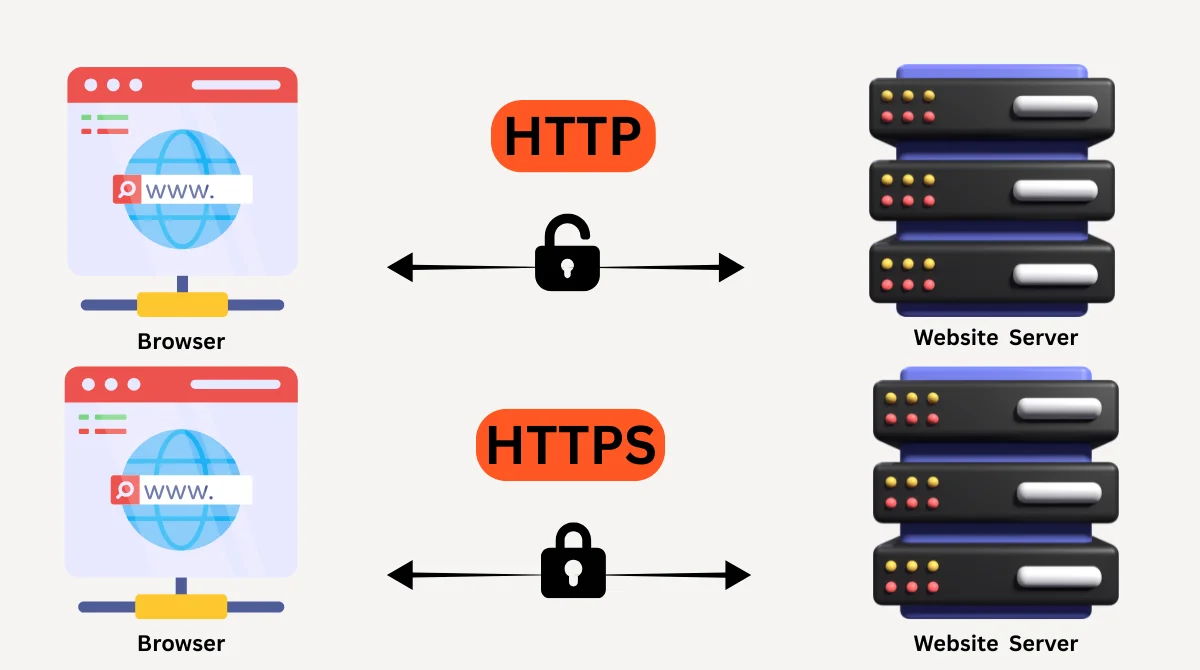
6. HTTPS and SSL Certificates
Security is a ranking factor, and users trust secure sites more. Implement SSL certificates to enable HTTPS, ensure all pages load over HTTPS, set up proper 301 redirects from HTTP to HTTPS, fix mixed content warnings, and update internal links to use HTTPS.
7. Canonical Tags
Prevent duplicate content issues by specifying the preferred version of a page. Implement canonical tags on pages with similar or duplicate content, use self-referencing canonicals as best practice, ensure canonical URLs are consistent with your XML sitemap, and avoid chains of canonical tags.
8. Structured Data (Schema Markup)
Help search engines understand your content and enable rich results. Implement relevant schema types (Article, Product, Recipe, FAQ, etc.), use JSON-LD format (Google’s preferred method), test markup using Google’s Rich Results Test, and keep structured data updated with page content.
9. Broken Links and Error Handling
Broken links and crawl errors harm user experience and SEO performance. Regular checks for 404 errors and redirect issues keep the website healthy and easy to crawl.
10. Core Web Vitals
These user-centric performance metrics are ranking factors. Monitor and optimize Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – aim for under 2.5 seconds, First Input Delay (FID) – aim for under 100 milliseconds, and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – aim for under 0.1. Use Google PageSpeed Insights and Search Console to track these metrics.
11. JavaScript SEO
Ensure JavaScript-rendered content is accessible to search engines. Use server-side rendering (SSR) or static site generation when possible, implement dynamic rendering for search engine bots if needed, avoid blocking important resources, test how Google renders your pages using the URL Inspection tool, and ensure critical content is visible in initial HTML.
Why Technical SEO Matters?
Even the best content fails if search engines cannot read it. Technical SEO ensures accessibility to bots and prevents ranking losses caused by hidden errors.
Key benefits include:
- Faster indexing and ranking improvements.
- Better user experience across devices.
- Protection from traffic drops during site updates.
- Support for global supply chain pages, pricing updates, and retailer information.
In many cases, fixing technical issues can create immediate ranking improvements, especially for established websites.
Technical SEO Examples
Technical SEO examples demonstrate practical applications. Fixing a slow server response time might involve upgrading hosting or enabling caching. Implementing lazy loading for images reduces initial page load, improving Core Web Vitals scores.
Creating a proper XML sitemap and submitting it through Google Search Console helps search engines discover new content faster. Setting up 301 redirects for old URLs preserves link equity when you restructure your site.
Adding schema markup to product pages enables rich snippets in search results, potentially increasing click-through rates. Mobile optimization might involve responsive design changes or accelerated mobile pages (AMP) implementation.
On Page SEO vs Technical SEO: Key Differences
Understanding the differences helps you allocate time, capital, and resources wisely.
Focus Area
On-page SEO focuses on content and HTML elements visible to users. You’re optimizing what people read, watch, and interact with. Technical SEO focuses on site infrastructure invisible to most visitors. You’re optimizing how servers deliver content and how bots process it.
The mission of on-page SEO is relevance matching content to search queries. The mission of technical SEO is accessibility ensuring bots can find and understand your site.
Who Handles Each Type?
Content writers, marketers, and SEO specialists typically handle on-page optimization. These activities require understanding keywords, user intent, and content strategy. Most on-page tasks don’t require coding knowledge.
Technical SEO often requires developers or specialized technical SEO consultants. Tasks involve server configurations, code modifications, and platform-specific adjustments. The skill level needed is higher, and mistakes can break functionality.
Implementation Timeline
On-page SEO requires regular updates. Content needs refreshing, keywords evolve, and user expectations change. You’ll continuously optimize existing pages while creating new ones.
Technical SEO typically involves one-time fixes plus monitoring. Once you resolve crawl errors or improve site speed, those fixes remain in place. However, ongoing monitoring catches new issues before they cause ranking drops.
Comparison Table
| Factor | On Page SEO | Technical SEO |
| What It Controls | Content and HTML | Site infrastructure |
| Main Goal | Relevance to searches | Accessibility to bots |
| Skill Level | Beginner friendly | Requires technical knowledge |
| Tools Needed | Keyword research, content tools | Developer tools, testing platforms |
| Update Frequency | Regular updates | One-time fixes plus monitoring |
| Impact Speed | Medium term | Can be immediate |
Which One Should You Prioritize First
The right starting point depends on your current site condition.
Start with Technical SEO If
You should prioritize technical SEO if:
- Your site loads slowly or fails mobile tests.
- Pages are not indexed.
- You recently migrated or redesigned your site.
- You see crawl errors in search console.
These issues block growth regardless of content quality.
Start with On Page SEO If
On page SEO should come first if:
- Your site is technically sound.
- Content does not match search intent.
- Rankings are stuck despite traffic.
- Product pages lack clarity or value.
Improving content can increase conversions, net sales, and overall results.
You Need Both If
Most websites need both. Technical SEO creates the foundation, while on page SEO builds authority and relevance on top of it.
How On Page SEO and Technical SEO Work Together?
On-page SEO and technical SEO function as complementary forces. Neither alone produces optimal results. Understanding their relationship helps you create an integrated strategy.
Technical SEO Enables On-Page Success
Technical SEO creates the conditions where on-page optimization can succeed. Fast page speeds keep users engaged with your content. Mobile optimization ensures your well-crafted pages display correctly on all devices.
Proper indexing means search engines actually see your optimized content. Without technical foundations, your on-page efforts remain invisible to both bots and users.
On-Page SEO Maximizes Technical Foundation
On-page SEO maximizes what technical work makes possible. A perfectly crawlable site with terrible content won’t rank. On-page optimization turns technical accessibility into actual rankings and traffic.
Quality content encourages backlinks and social shares. This amplifies the reach of your technically sound website.
Real-World Example
Consider an online shop selling premium products. Technical SEO ensures fast loading, secure checkout, and mobile functionality. Product pages load in under 2 seconds. Google can crawl and index the entire product catalog.
On-page SEO then optimizes each product page for relevant searches. Unique descriptions target specific keywords. Internal links connect related products. Category pages feature helpful buyer guides.
Together, these efforts create a site that ranks well and converts visitors into customers. Neither approach alone would produce the same results.
Common On Page SEO Mistakes to Avoid
- Keyword Stuffing: Overusing keywords damages readability and trust. Search engines prefer natural language and context.
- Duplicate Content: Duplicate pages confuse bots and weaken rankings. Always create unique, valuable content.
- Thin Content: Pages without depth fail to build authority. Explain topics fully, whether discussing pricing, products, or investor outlook.
- Ignoring Search Intent: Content must match what users want. Informational searches require education, not sales language.
Common Technical SEO Mistakes to Avoid
- Blocking Pages with Robots.txt: Accidentally blocking key pages can remove them from search results.
- Slow Server Response Times: Slow servers increase bounce rates and hurt rankings.
- Broken Internal Links: Broken links waste crawl budget and frustrate users.
- Missing Mobile Optimization: Most traffic comes from mobile. Without optimization, rankings suffer.
Tools to Improve Both SEO Types
The right tools make optimization more effective and efficient. Different tools serve different purposes across both SEO types.
Technical SEO Tools
- Google Search Console monitors indexing and crawl issues.
- PageSpeed Insights measures loading performance.
- Screaming Frog crawls sites to identify technical problems.
- GTmetrix provides detailed speed analysis.
- Mobile-Friendly Test checks mobile compatibility.
For on-page optimization, use keyword research platforms, content analysis tools, and rank tracking software. These help you identify opportunities and measure results over time.
Step-by-Step Action Plan for Beginners
This four-week action plan provides structure for beginners tackling SEO. Follow each week’s activities in order for best results.
Week 1: Technical Foundation
Focus the first week on technical essentials. Set up Google Search Console and submit your sitemap. Check for crawl errors and fix any blocking issues. Test page speed and implement basic improvements.
Verify mobile functionality across devices. Ensure HTTPS works properly. Address any security warnings.
Week 2: On-Page Basics
Week two shifts to on-page fundamentals. Conduct keyword research for your main pages. Optimize title tags and meta descriptions. Review and improve header tag structure.
Ensure each page has unique, descriptive content. Add alt text to images. Create a consistent URL structure.
Week 3: Content Enhancement
Week three focuses on content quality. Expand thin pages with additional information. Add internal links between related content. Update outdated statistics and examples.
Consider adding new content that addresses gaps in your topic coverage. Focus on matching search intent.
Week 4: Technical Cleanup
Week four involves technical refinement. Run a complete site audit to catch remaining issues. Fix broken links and redirect chains. Optimize remaining slow pages.
Set up ongoing monitoring to catch future problems quickly.
FAQ
1. Which is more important: On-Page SEO or Technical SEO?
Both are equally important. Technical SEO creates the foundation, and on-page SEO builds value on top of it. Without technical SEO, content may not rank, and without on-page SEO, traffic may not convert.
2. Can a website rank with good On-Page SEO but weak Technical SEO?
It may rank temporarily, but long-term performance suffers. Crawl errors, slow speed, or poor mobile experience can limit rankings even if content is high quality.
3. Can On-Page SEO improve rankings without backlinks?
Yes, strong on-page SEO can improve rankings, especially for low to medium competition keywords, but backlinks help strengthen authority.
4. Which SEO should be done first for a new website?
Technical SEO should come first to ensure proper indexing, then on-page SEO should be applied to optimize content and keywords.
5. Can On-Page SEO fix indexing issues?
No. Indexing issues require technical SEO fixes like sitemap updates, robots.txt adjustments, and proper canonical usage.
Conclusion
On page SEO and technical SEO are not competitors they are partners. One focuses on relevance, clarity, and value for humans. The other ensures search engines can access and understand that value. Ignoring either leads to missed opportunities, wasted effort, and slower growth.
For long-term success, start with a strong technical foundation. Fix crawl issues, improve speed, and ensure mobile usability. Then invest in high-quality on page SEO that speaks clearly to your audience, reflects your brand today, and supports your business goals.
Whether you manage an apparel retailer, a global brand, or a content-driven website, combining both strategies delivers sustainable results. SEO is not about quick wins it is about building trust, authority, and visibility over time. When done right, the impact compounds year after year.