- What is Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical?
- Why Does This Issue Occur?
- How to Identify the Problem?
- Step-by-Step Solutions
- Best Practices for Prevention
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Technical Implementation Methods
- Monitoring and Maintenance
- Expected Results and Timeline
- Advanced Solutions
- Conclusion
What is Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical?
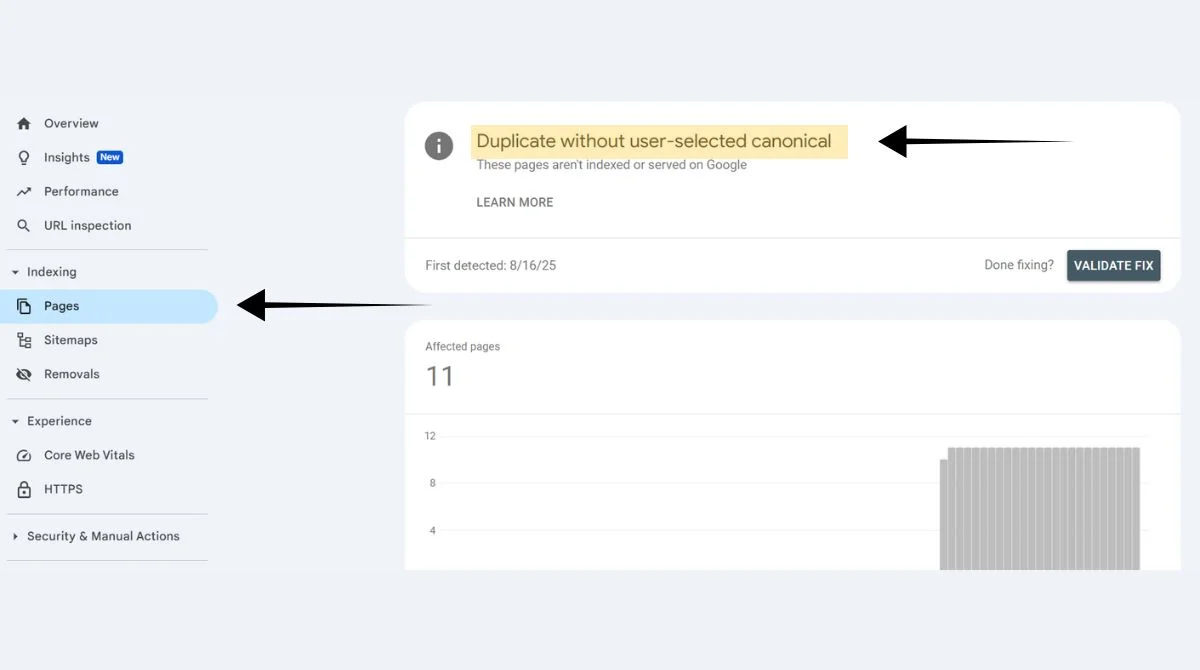
The “Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical” issue appears in Google Search Console when your website has duplicate content pages without proper canonical tags. Google finds duplicate content on your site, but cannot detect a canonical tag telling it which version to index.
This means Google has to make its own choice about which page to show in search results. Sometimes this choice doesn’t match your preference, leading to SEO problems.
Why Does This Issue Occur?
Several factors can trigger this problem on your website:
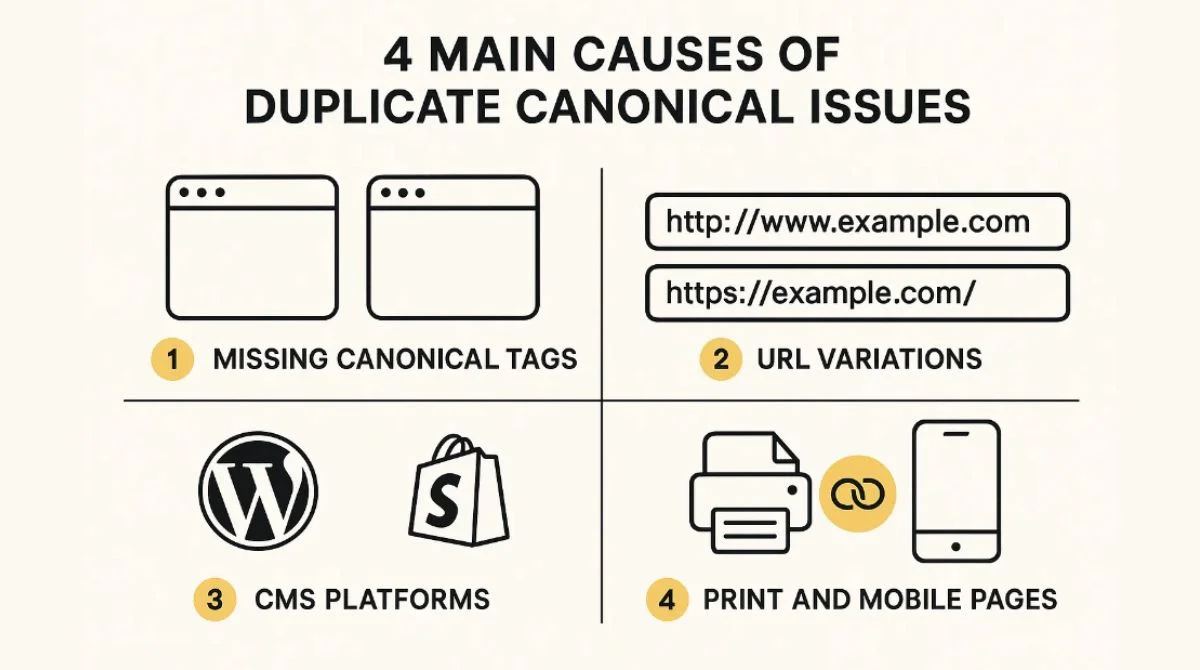
Missing Canonical Tags
Your pages lack the rel=”canonical” attribute that tells search engines which version is the main one. Without this guidance, Google treats all similar pages as separate entities.
URL Variations
Different URL formats for the same content create confusion. Common examples include HTTP vs HTTPS versions, trailing slash variations, and parameter-based URLs.
Content Management Systems
WordPress, Shopify, and other CMS platforms sometimes generate multiple URLs for identical content. Product pages, category listings, and blog posts often face this issue.
Print-Friendly Pages
Websites offering print versions or mobile-optimized pages without canonical tags create duplicate content scenarios.
How to Identify the Problem?
Check Google Search Console
Navigate to the Coverage report in your Search Console account. Look for the “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” status under excluded pages.
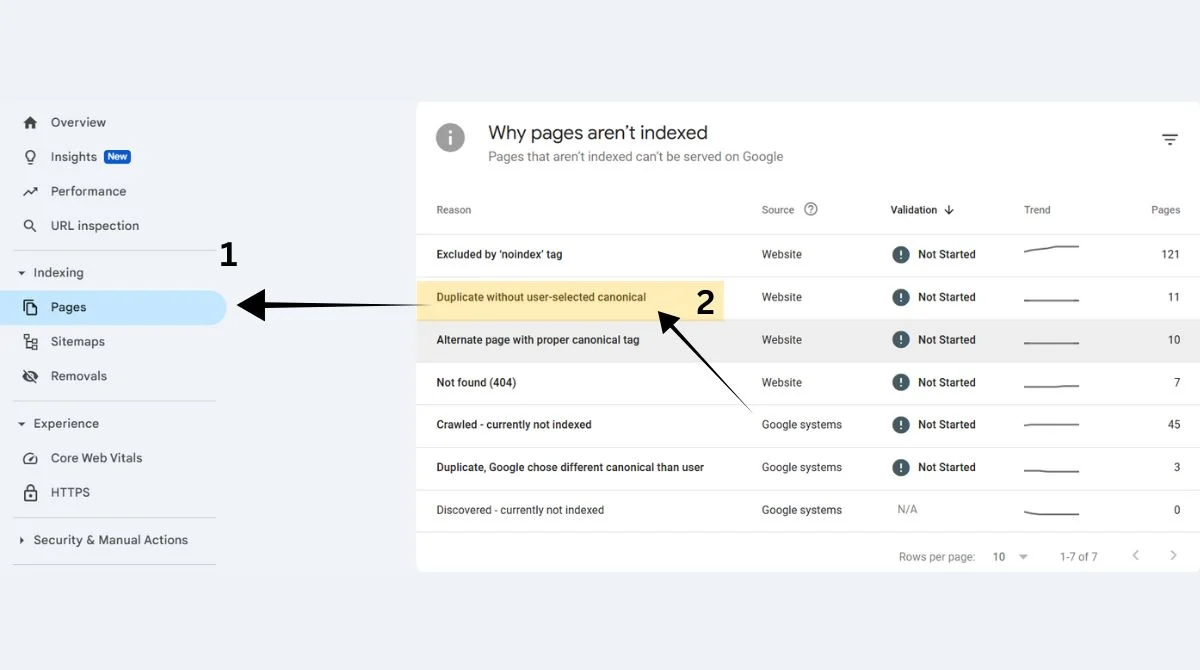
Review Your URLs
Examine your website structure for similar content accessible through different URLs. Pay attention to parameter variations and trailing slashes.
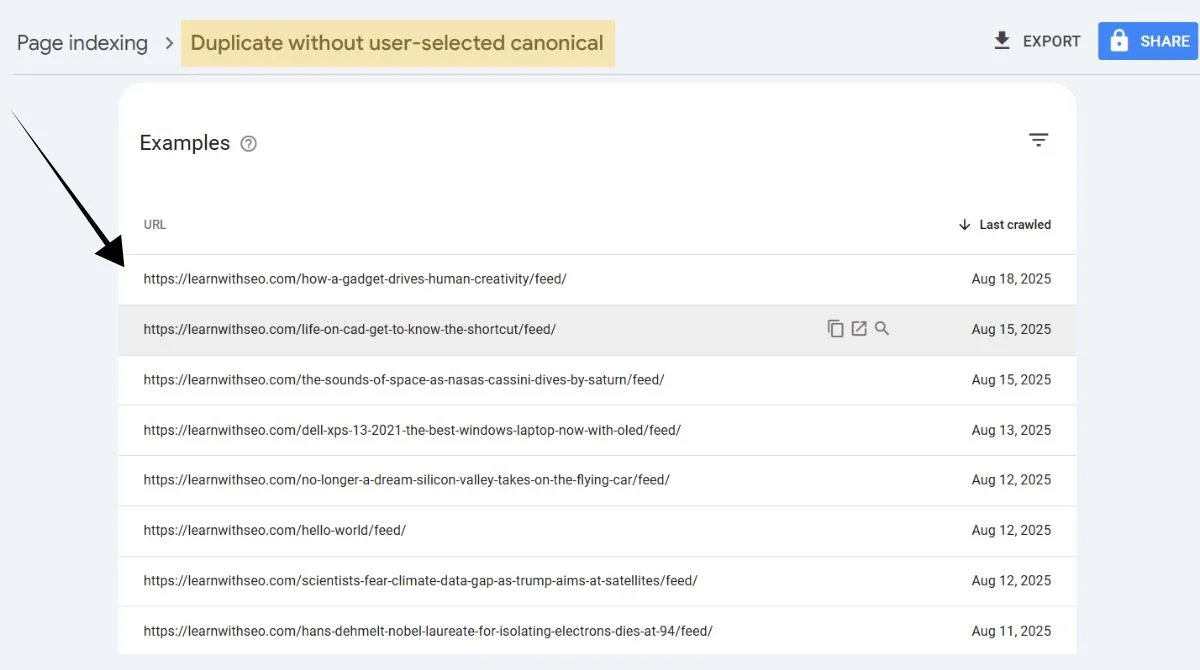
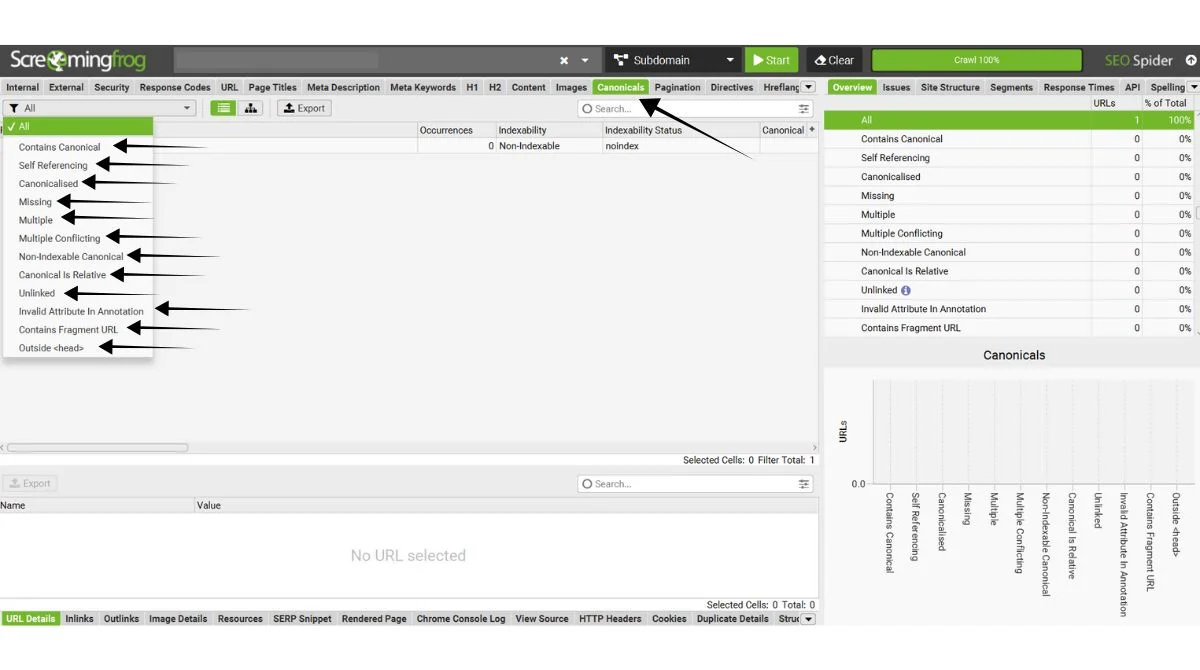
Use SEO Tools
Tools like Screaming Frog, SEMrush, or Ahrefs can crawl your site and identify duplicate content issues automatically.
Step-by-Step Solutions
1. Add Self-Referencing Canonical Tags
Adding self-referencing canonical tags points Google to the pages themselves, ensuring search engines won’t separately index duplicates.
For each page, add this code in the HTML head section:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://yourwebsite.com/page-url/" />
2. Implement Proper Canonical Tags
Choose your preferred version and add canonical tags pointing to it from all duplicate pages.
Example: If you prefer the HTTPS version with a trailing slash:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/product/" />
Add this tag to all variations:
-
http://example.com/product
-
https://example.com/product
-
https://example.com/product/
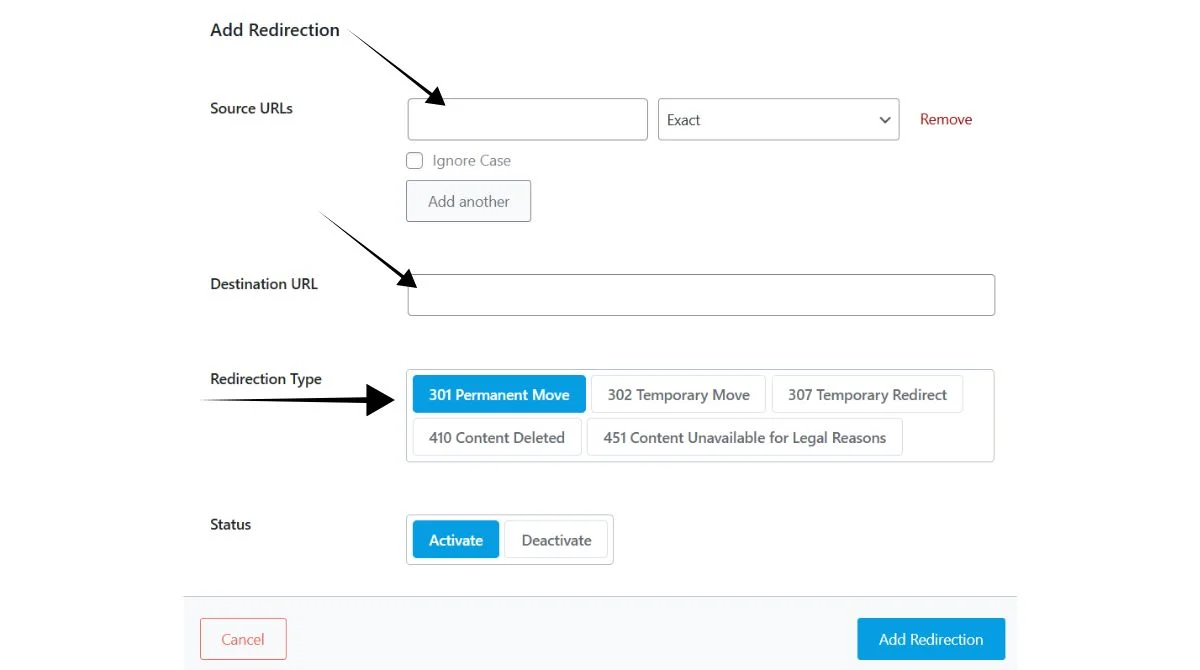
3. Use 301 Redirects
Create 301 redirects for duplicate pages to consolidate link equity and eliminate duplicate content. This method works well when you don’t need multiple versions of the same content.
4. Configure Your CMS Settings
WordPress Solutions
- Install SEO plugins like Yoast or RankMath.
- Enable canonical URL settings.
- Configure the permalink structure consistently.
Shopify Solutions
- Use built-in canonical tag features.
- Avoid creating duplicate product pages.
- Manage collection page variations properly.

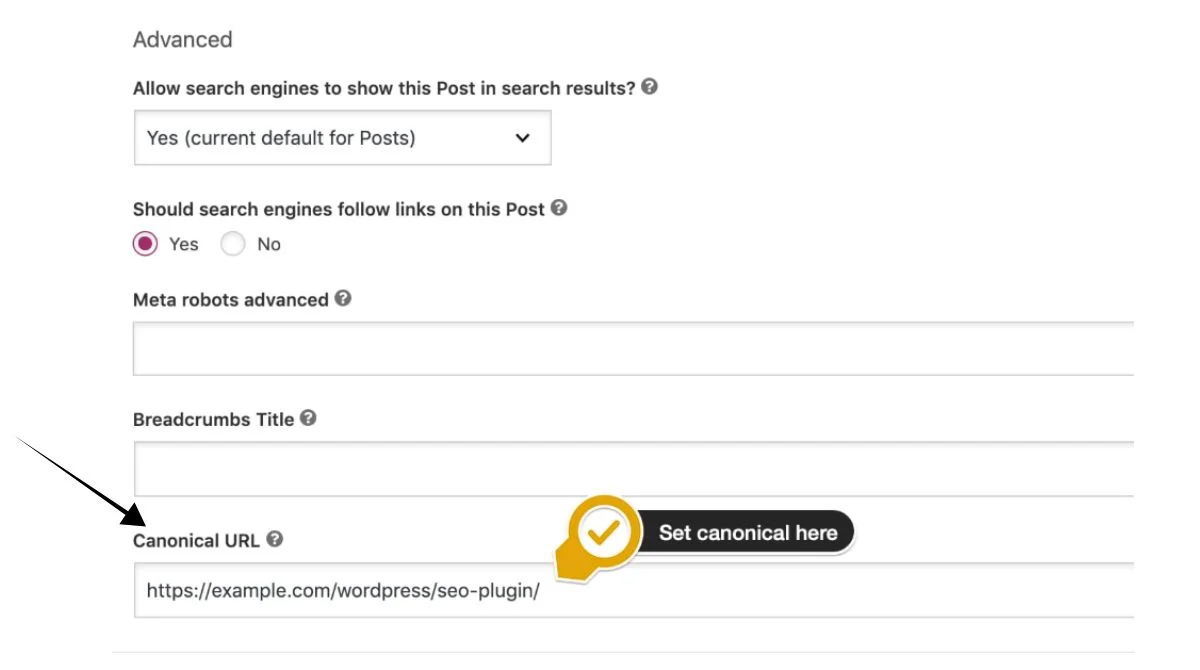
5. Handle URL Parameters
For pages with tracking parameters or filters, use canonical tags to point to the clean version:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/category/" />
This works for URLs like:
-
example.com/category/?utm_source=email
-
example.com/category/?color=red&size=large
Best Practices for Prevention
- Maintain Consistency: Current best practices include canonicalizing every page on your site, even though Google says it isn’t mandatory. Use the same URL format throughout your website. Choose either trailing slashes or no slashes and stick to it.
- Update Your Sitemap: Include only canonical URLs in your XML sitemap. This reinforces your preferred page versions to search engines.
- Monitor Internal Links: Ensure internal links point to canonical versions of pages. Mixed linking patterns confuse both users and search engines.
- Regular Audits: Perform monthly checks for new duplicate content issues. Growing websites often develop these problems over time.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Multiple Canonical Tags: Only specify one canonical URL per page to avoid confusing Google. Multiple canonical tags on the same page create conflicting signals.
- Incorrect URL Format: Always use absolute URLs with the full domain name. Relative URLs in canonical tags can cause implementation errors.
- Pointing to Non-Existent Pages: Ensure canonical URLs point to accessible, indexed pages. Broken canonical links harm your SEO performance.
- Ignoring HTTPS/HTTP Consistency: Implement 301 redirects to the correct version or add canonical tags that reference the HTTPS version on HTTP pages.
Technical Implementation Methods
HTML Method
Add canonical tags directly in your page’s HTML head section. This method works for all website types and provides direct control.
HTTP Header Method
For non-HTML files like PDFs, use HTTP header canonicalization:
Link: <https://example.com/preferred-version>; rel="canonical"
Sitemap Method
List only canonical URLs in your sitemap.xml file. This method supports but doesn’t replace HTML canonical tags.
Monitoring and Maintenance
- Track GSC Reports: Check your Google Search Console coverage reports weekly. Look for improvements in indexed pages and reductions in duplicate content warnings.
- Set Up Alerts: Configure monitoring tools to alert you when new duplicate content issues appear on your website.
- Document Your Strategy: Keep records of your canonical tag decisions. This helps maintain consistency as your website grows.
Expected Results and Timeline
- Initial Improvements: Most websites see improvements in Search Console reports within 2-4 weeks of implementing proper canonical tags.
- Full Resolution: Complete resolution of duplicate content issues typically takes 1-3 months, depending on your website’s crawl frequency and size.
- Long-term Benefits: Properly implemented canonical tags improve your website’s search engine rankings, user experience, and technical SEO health.
Advanced Solutions
International Websites
Use hreflang tags alongside canonical tags for multi-language websites. This prevents duplicate content issues across different language versions.

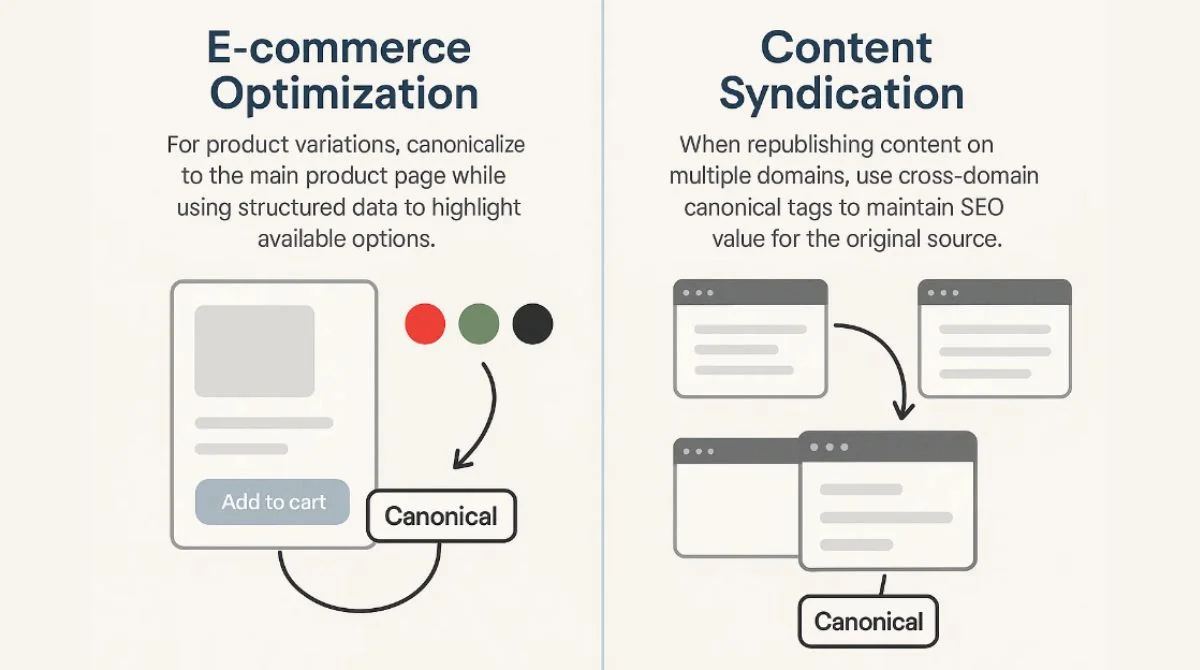
E-commerce Optimization
For product variations, canonicalize to the main product page while using structured data to highlight available options.
Content Syndication
When republishing content on multiple domains, use cross-domain canonical tags to maintain SEO value for the original source.
Conclusion
Fixing the “Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical” issue requires proper canonical tag implementation and consistent URL structure. Start by identifying duplicate pages, then add appropriate canonical tags or 301 redirects. Regular monitoring through Google Search Console helps maintain long-term SEO health. Results typically appear within 2-4 weeks of implementation.