- What Are Internal Links?
- The Magic Number: How Many Internal Links Per Page?
- Why Internal Links Matter for SEO?
- Best Practices for Internal Linking
- Common Internal Linking Mistakes
- Strategic Internal Linking Framework
- Tools for Internal Link Analysis
- Measuring Internal Linking Success
- Advanced Internal Linking Strategies
- Technical Considerations
- Conclusion
Internal linking plays a crucial role in your website’s SEO performance. Many website owners wonder about the perfect number of internal links to include on each page. This guide provides expert insights and actionable strategies to help you optimize your internal linking structure.
What Are Internal Links?
Internal links connect different pages within your website. They help users navigate your content and allow search engines to understand your site structure. Unlike external links that point to other websites, internal links keep visitors on your domain.
These links pass link equity (also called link juice) between pages. This helps distribute authority throughout your website and can improve rankings for important pages.

The Magic Number: How Many Internal Links Per Page?
SEO experts recommend 5-10 internal links per 2,000 words of content. This translates to approximately one link every 200-300 words.
However, the exact number depends on several factors:
Content Length Guidelines
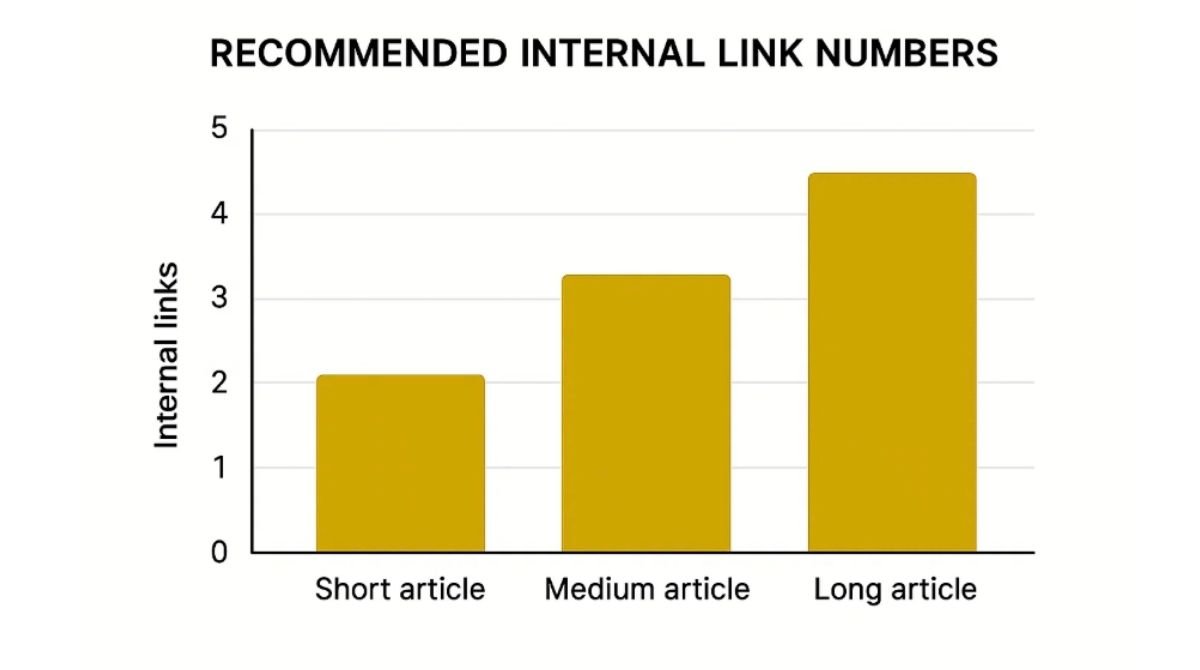
- Short articles (500-800 words): 2-4 internal links.
- Medium articles (800-1,500 words): 3-7 internal links.
- Long articles (1,500+ words): 5-12 internal links.
Google’s Official Stance
Google states there’s no magical ideal number of links a given page should have. The search giant emphasizes relevance and user value over specific quantities.
However, Google recommends keeping total links under 150 per page to maintain link equity effectiveness. Pages with excessive links may see diluted PageRank distribution.
Why Internal Links Matter for SEO?
1. Improved Crawlability
Google’s crawlers use internal links to discover and index new content. Well-structured internal linking helps search engines understand your site architecture.
2. Link Equity Distribution
Internal links pass authority from high-performing pages to newer or less visible content. This helps improve rankings across your entire website.
3. Enhanced User Experience
Strategic internal linking keeps visitors engaged longer. It reduces bounce rates and increases time on site – both positive ranking signals.
Best Practices for Internal Linking
Link Placement Strategy
Place your most important internal links at the top of your pages where they’re most visible. Users typically scan content from top to bottom.
Consider these prime locations:
- Within the first paragraph.
- In heading sections.
- Throughout the main content body.
- In the conclusion sections.
Anchor Text Optimization
Use descriptive, meaningful anchor text for links. Avoid generic phrases like “click here” or “read more.” Instead, use keywords that describe the linked content.
Good examples:
- “SEO keyword research tools”
- “WordPress security best practices”
- “Content marketing strategies“
Relevance is Key
Only link to pages that provide additional value to readers. Link to the most relevant and valuable content users would want to see next. Irrelevant links confuse both users and search engines.

Common Internal Linking Mistakes
- Over-Optimization: Stuffing too many internal links can hurt your rankings. Google doesn’t crawl pages with over 150 links effectively. Focus on quality over quantity.
- Using the Same Anchor Text Repeatedly: Vary your anchor text to avoid appearing manipulative. Using identical phrases repeatedly can trigger spam filters.
- Linking to Irrelevant Pages: Random internal links provide no value. Each link should enhance the user’s understanding or provide logical next steps.
- Forgetting About New Content: Make sure every new page has at least 2-3 internal links pointing to it. Orphaned pages struggle to gain visibility and rankings.
Strategic Internal Linking Framework
Hub and Spoke Model
Create pillar content (hubs) that cover broad topics. Link related articles (spokes) to these authoritative pages. This structure helps establish topical authority.
Topic Clusters
Group related content into clusters. Link pages within the same topic cluster to strengthen thematic relevance. This approach aligns with Google’s preference for expertise and topical depth.
Regular Auditing
Run regular audits to catch new internal linking issues. Schedule monthly reviews to maintain a healthy site structure and identify optimization opportunities.

Tools for Internal Link Analysis
Several tools can help optimize your internal linking strategy:
- Google Search Console: Identifies crawling issues.
- Screaming Frog: Analyzes site structure and link distribution.
- Ahrefs Site Audit: Provides comprehensive internal linking reports.
- SEMrush: Offers detailed internal linking analysis.

Measuring Internal Linking Success
Key Metrics to Track
Monitor these indicators to gauge your internal linking effectiveness:
- Organic traffic growth: Improved internal linking should boost overall visibility.
- Page views per session: Better linking increases user engagement.
- Bounce rate reduction: Relevant links keep visitors on your site.
- Crawl efficiency: Faster indexing of new content.
Long-term Benefits
Consistent internal linking optimization delivers cumulative benefits. Pages gain authority over time, leading to improved rankings and increased organic traffic.
Advanced Internal Linking Strategies
Contextual Linking
Embed links naturally within content flow. Contextual links perform better than standalone link lists or forced placements.
Deep Linking
Don’t just link to the homepage or main category pages. Link directly to specific, relevant content that adds value to the current topic.
Strategic Link Distribution
Distribute internal links based on page importance. Your most valuable pages should receive more internal links from other relevant content.

Technical Considerations
- Link Architecture: Create a link architecture that’s intuitive for users and crawlable for search engines. Important pages should be easily accessible from your homepage.
- Mobile Optimization: Ensure internal links work properly on mobile devices. Touch-friendly link sizes and proper spacing improve mobile user experience.
- Page Load Speed: Too many links can slow page loading. Balance comprehensive linking with optimal site performance.
Conclusion
The ideal number of internal links per page varies based on content length and purpose. For standard blog posts, 5-10 well-placed internal links work best. Remember that quality trumps quantity in internal linking. Focus on providing value to users rather than hitting specific numbers. Strategic, relevant links will always outperform excessive linking for SEO manipulation.