- What Is HTTP?
- How HTTP Works?
- The Problem with HTTP
- What Is HTTPS?
- How HTTPS Works?
- Why HTTPS Is Important Today?
- Key Differences Between HTTP and HTTPS
- How to Move from HTTP to HTTPS?
- How HTTPS Impacts SEO?
- Common Myths About HTTPS
- Future of HTTPS and Web Security
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Final Thoughts
When you browse the internet, you may have noticed that some websites start with HTTP while others begin with HTTPS. Though this single letter “S” might seem small, it makes a big difference in how safe and trustworthy a website is. In today’s online world, understanding the difference between HTTP and HTTPS isn’t just for web developers; it’s important for business owners, marketers, and everyday internet users, too.
What Is HTTP?
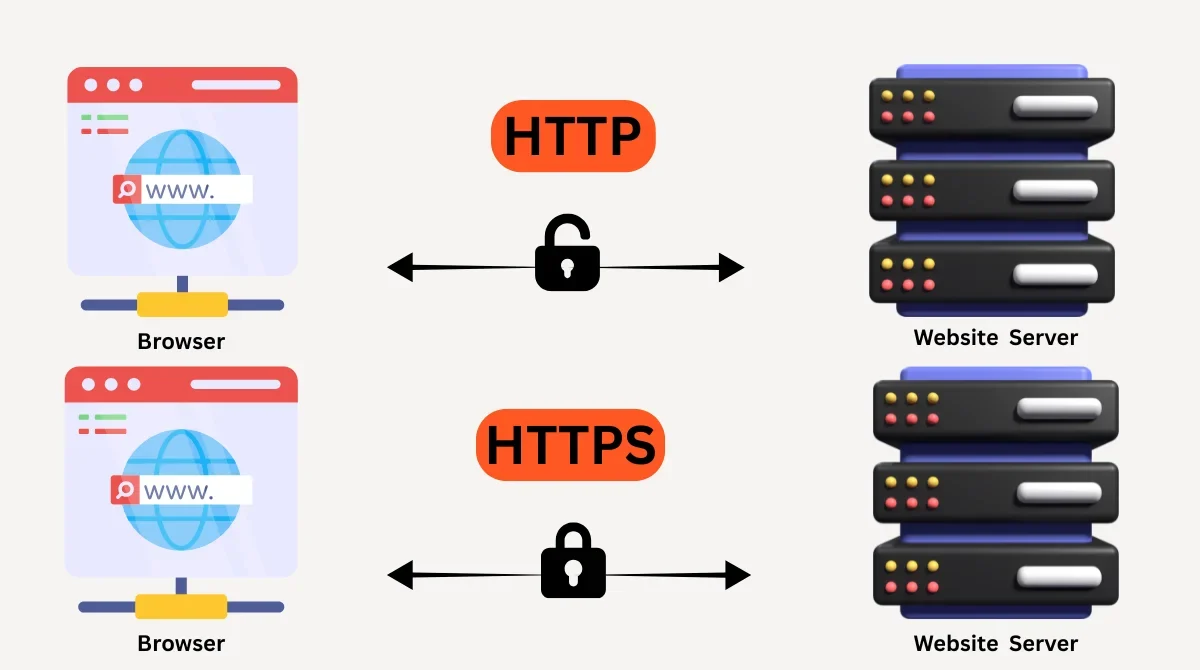
HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) is a system that allows communication between your browser and the web server. In simple terms, it helps load web pages from a server to your screen. When you type a web address like http://example.com, your browser requests the page from the server using HTTP, and the server sends back the requested data.
How HTTP Works?
- When you visit a site, your browser sends a request to the web server.
- The server replies with the page’s content (text, images, videos, etc.).
- Your browser displays it for you.
This exchange happens in plain text, which means that anyone who intercepts the connection, like a hacker or an internet provider, can see or manipulate the data. This is one of HTTP’s biggest flaws: it’s not secure.
The Problem with HTTP
HTTP was the standard in the early days of the web. But as online activities like e-commerce, online banking, and digital forms became common, security became a major concern.
Here’s what can go wrong with HTTP connections:
- Data Interception: Hackers can capture the information sent between your browser and the website.
- Data Modification: Attackers can change the content you receive, such as inserting malicious ads or code.
- No Authentication: There’s no guarantee that the website you’re visiting is actually what it claims to be.
Because of these risks, HTTP is now considered outdated for websites that handle sensitive data or any site that wants to be trusted by users.
What Is HTTPS?
HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure) is an upgraded, secure version of HTTP. The “S” stands for Secure, meaning that all communication between your browser and the web server is encrypted.
HTTPS uses an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer Security) certificate to protect the data transferred between the user and the website. This encryption ensures that even if someone intercepts the data, they won’t be able to read it.
How HTTPS Works?
- When you visit an HTTPS site, your browser requests the SSL certificate.
- The certificate proves that the site is genuine and owned by a verified entity.
- The browser and server create a secure, encrypted connection before exchanging any data.
This is why most secure sites, like banks or online stores, show a padlock icon in the browser bar next to the URL.
Why HTTPS Is Important Today?
HTTPS is no longer optional; it’s essential. Here’s why every website should use HTTPS:
1. Security & Encryption
HTTPS encrypts all data, protecting personal details like names, emails, and credit card numbers from hackers or eavesdroppers. This keeps users safe and prevents identity theft or data breaches.
2. Trust & Credibility
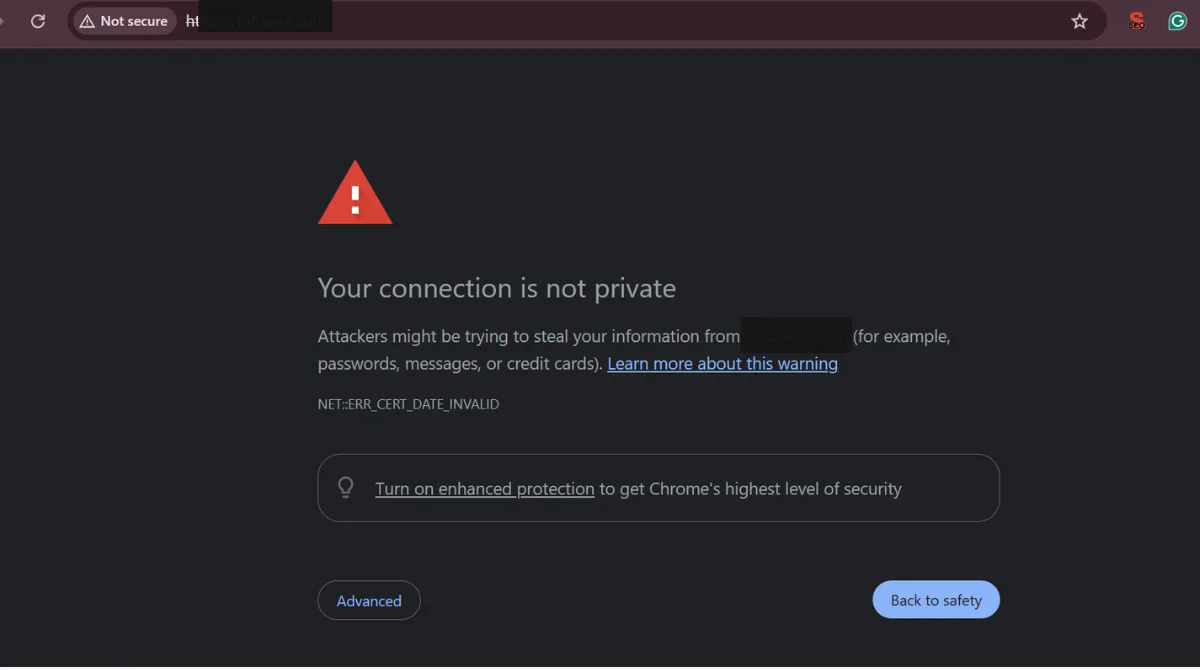
When users see the padlock icon, they feel more confident sharing information or making purchases. A site without HTTPS may display a “Not Secure” warning, which can scare visitors away instantly.
3. Better SEO Rankings
Google uses HTTPS as a ranking factor. Websites with HTTPS are considered more trustworthy, giving them an SEO advantage over HTTP sites. This is especially important for businesses focused on search engine optimization (SEO).
4. Data Integrity
HTTPS ensures that your website’s data isn’t altered or injected with unwanted ads or scripts while being transferred. It helps maintain the integrity of your content, which is vital for brand credibility.
5. Faster Performance
With modern technologies like HTTP/2, HTTPS sites often load faster than HTTP sites. Google prioritizes fast, secure websites for a better user experience.
Key Differences Between HTTP and HTTPS
| Feature | HTTP | HTTPS |
| Full Form | HyperText Transfer Protocol | HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure |
| Security | Not Secure | Fully Encrypted |
| Data Encryption | No | Yes, with SSL/TLS |
| URL Prefix | http:// | https:// |
| SEO Ranking | Lower | Higher |
| Browser Indication | “Not Secure” warning | Padlock icon |
| Performance (HTTP/2) | Slower | Faster |
| Data Integrity | Vulnerable | Protected |
How to Move from HTTP to HTTPS?
If your website still uses HTTP, it’s time to migrate to HTTPS. Here’s how you can do it properly:
1. Get an SSL Certificate
Purchase an SSL certificate from a trusted provider (like Let’s Encrypt, Namecheap, or Cloudflare). Many hosting companies even offer free SSL certificates.
2. Install the SSL Certificate
Once you get the certificate, install it on your web hosting server. Your hosting provider usually provides a step-by-step guide for this process.
3. Update Website Links
Change all internal links, images, scripts, and CSS files from http:// to https:// to prevent mixed-content warnings.
4. Use 301 Redirects
Redirect all old HTTP pages to their new HTTPS versions using 301 redirects. This informs search engines that your site has been permanently relocated.
5. Update Canonical Tags
Update your canonical tags to use the HTTPS version. This helps avoid duplicate content issues after migration.
Also, set your hreflang canonical and canonical hreflang tags correctly if your website supports multiple languages. This ensures that Google serves the right localized version of your pages.
6. Update Google Search Console & Analytics
Add your new HTTPS version to Google Search Console and Google Analytics to continue tracking your website’s performance.
7. Check for Mixed Content Issues
After migration, test your pages using tools like Why No Padlock or SSL Labs to ensure all resources are loading securely.
How HTTPS Impacts SEO?
Using HTTPS benefits your SEO in several ways:
- Ranking Boost: Google gives preference to HTTPS sites over HTTP ones.
- Higher Click-Through Rate (CTR): Users are more likely to click on secure websites in search results.
- Reduced Bounce Rate: Visitors stay longer on secure sites they trust.
- Better Referral Data: When traffic passes through HTTPS to HTTPS, referral data is preserved, which helps in accurate analytics.
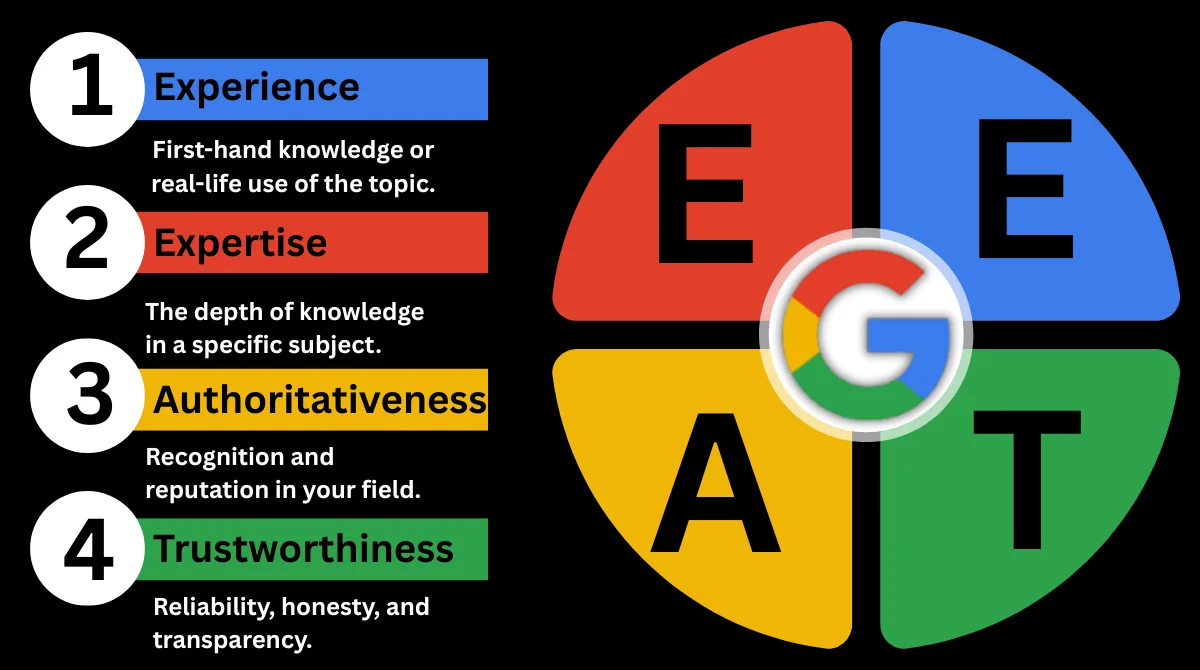
Moreover, HTTPS builds E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness), a key factor in Google’s ranking system. Websites that show technical reliability (like HTTPS) demonstrate trust and professionalism to both users and search engines.
Common Myths About HTTPS
Let’s clear a few misconceptions:
- Myth 1: “HTTPS is only for e-commerce sites.”
→ Wrong. Every site that collects data (like contact forms or newsletter signups) needs HTTPS. - Myth 2: “HTTPS slows down websites.”
→ Not true anymore. With HTTP/2, HTTPS often improves page speed. - Myth 3: “It’s hard to install SSL.”
→ Most hosting providers automate SSL installation within minutes. - Myth 4: “Free SSL certificates aren’t safe.”
→ Free certificates from trusted authorities like Let’s Encrypt are perfectly secure.
Future of HTTPS and Web Security
The web is moving toward a fully encrypted environment. Search engines, browsers, and users now expect HTTPS as the default standard. Google Chrome and Firefox already flag non-secure sites, pushing the entire web toward better security.
In the future, technologies like HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security) and Certificate Transparency will further strengthen website authenticity. Businesses that fail to adapt risk losing both traffic and trust.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why should I switch my website to HTTPS?
Switching to HTTPS improves your site’s security, builds user trust, enhances SEO rankings, and ensures your data remains private and unaltered during transfer.
2. Is HTTPS required for SEO?
Yes. Google confirmed that HTTPS is a ranking signal. Websites with HTTPS are more likely to appear higher in search results compared to non-secure sites.
3. Does HTTPS make a website faster?
Yes. With HTTP/2 technology, HTTPS-enabled sites generally load faster and perform better than HTTP ones, improving user experience and SEO.
4. Are free SSL certificates safe to use?
Absolutely. Free SSL certificates from trusted providers like Let’s Encrypt offer strong encryption and are fully recognized by browsers.
5. What happens if I don’t switch to HTTPS?
Web browsers will label your site as “Not Secure,” users may lose trust, and your SEO performance will likely suffer due to lower rankings and traffic loss.
Final Thoughts
The difference between HTTP and HTTPS is more than just a letter; it’s about trust, security, and credibility. Switching to HTTPS protects user data, boosts SEO rankings, improves website speed, and enhances your brand’s reputation. In today’s digital world, HTTPS isn’t optional; it’s essential. Whether you run a blog, business site, or online store, securing your site with HTTPS ensures visitors browse safely and confidently.